Page 62 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 62
01_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 11:46 am Page 42
42 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
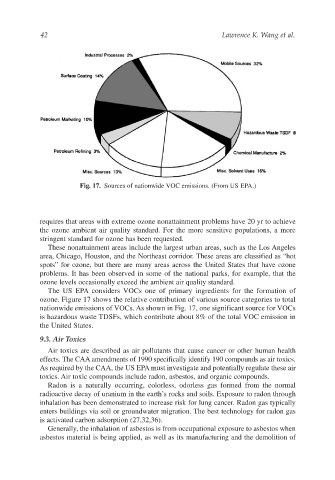
Fig. 17. Sources of nationwide VOC emissions. (From US EPA.)
requires that areas with extreme ozone nonattainment problems have 20 yr to achieve
the ozone ambient air quality standard. For the more sensitive populations, a more
stringent standard for ozone has been requested.
These nonattainment areas include the largest urban areas, such as the Los Angeles
area, Chicago, Houston, and the Northeast corridor. These areas are classified as “hot
spots” for ozone, but there are many areas across the United States that have ozone
problems. It has been observed in some of the national parks, for example, that the
ozone levels occasionally exceed the ambient air quality standard.
The US EPA considers VOCs one of primary ingredients for the formation of
ozone. Figure 17 shows the relative contribution of various source categories to total
nationwide emissions of VOCs. As shown in Fig. 17, one significant source for VOCs
is hazardous waste TDSFs, which contribute about 8% of the total VOC emission in
the United States.
9.3. Air Toxics
Air toxics are described as air pollutants that cause cancer or other human health
effects. The CAA amendments of 1990 specifically identify 190 compounds as air toxics.
As required by the CAA, the US EPA must investigate and potentially regulate these air
toxics. Air toxic compounds include radon, asbestos, and organic compounds.
Radon is a naturally occurring, colorless, odorless gas formed from the normal
radioactive decay of uranium in the earth’s rocks and soils. Exposure to radon through
inhalation has been demonstrated to increase risk for lung cancer. Radon gas typically
enters buildings via soil or groundwater migration. The best technology for radon gas
is activated carbon adsorption (27,32,36).
Generally, the inhalation of asbestos is from occupational exposure to asbestos when
asbestos material is being applied, as well as its manufacturing and the demolition of