Page 26 - Algae
P. 26
General Overview 9
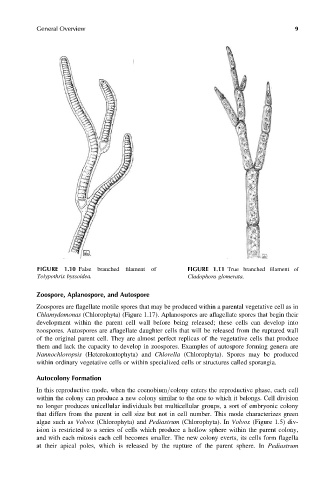
FIGURE 1.10 False branched filament of FIGURE 1.11 True branched filament of
Tolypothrix byssoidea. Cladophora glomerata.
Zoospore, Aplanospore, and Autospore
Zoospores are flagellate motile spores that may be produced within a parental vegetative cell as in
Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyta) (Figure 1.17). Aplanospores are aflagellate spores that begin their
development within the parent cell wall before being released; these cells can develop into
zoospores. Autospores are aflagellate daughter cells that will be released from the ruptured wall
of the original parent cell. They are almost perfect replicas of the vegetative cells that produce
them and lack the capacity to develop in zoospores. Examples of autospore forming genera are
Nannochloropsis (Heterokontophyta) and Chlorella (Chlorophyta). Spores may be produced
within ordinary vegetative cells or within specialized cells or structures called sporangia.
Autocolony Formation
In this reproductive mode, when the coenobium/colony enters the reproductive phase, each cell
within the colony can produce a new colony similar to the one to which it belongs. Cell division
no longer produces unicellular individuals but multicellular groups, a sort of embryonic colony
that differs from the parent in cell size but not in cell number. This mode characterizes green
algae such as Volvox (Chlorophyta) and Pediastrum (Chlorophyta). In Volvox (Figure 1.5) div-
ision is restricted to a series of cells which produce a hollow sphere within the parent colony,
and with each mitosis each cell becomes smaller. The new colony everts, its cells form flagella
at their apical poles, which is released by the rupture of the parent sphere. In Pediastrum