Page 71 - An Introduction to Analytical Atomic Spectrometry - L. Ebdon
P. 71
Page 53
cup for AFS are shown in Fig. 3.2. Using a power supply of 400 A at 10 V, the furnace could be heated
to 2600°C in a few seconds. Typical solution volumes of 5-200 mm were used.
3
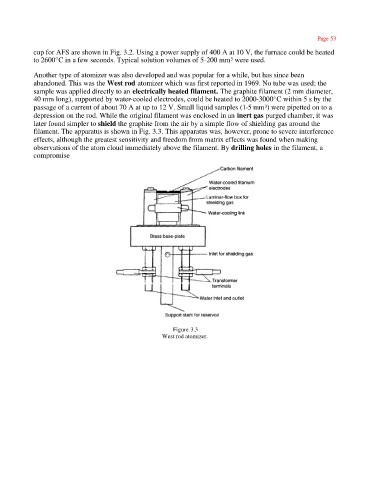
Another type of atomizer was also developed and was popular for a while, but has since been
abandoned. This was the West rod atomizer which was first reported in 1969. No tube was used; the
sample was applied directly to an electrically heated filament. The graphite filament (2 mm diameter,
40 mm long), supported by water-cooled electrodes, could be heated to 2000-3000°C within 5 s by the
passage of a current of about 70 A at up to 12 V. Small liquid samples (1-5 mm ) were pipetted on to a
3
depression on the rod. While the original filament was enclosed in an inert gas purged chamber, it was
later found simpler to shield the graphite from the air by a simple flow of shielding gas around the
filament. The apparatus is shown in Fig. 3.3. This apparatus was, however, prone to severe interference
effects, although the greatest sensitivity and freedom from matrix effects was found when making
observations of the atom cloud immediately above the filament. By drilling holes in the filament, a
compromise
Figure 3.3
West rod atomizer.