Page 230 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 230
different pump types, each motor has its advantages and disadvantages, which
determine suitability to particular applications. However, for AC motors, an inverter
must be included between the solar panels and the motor.
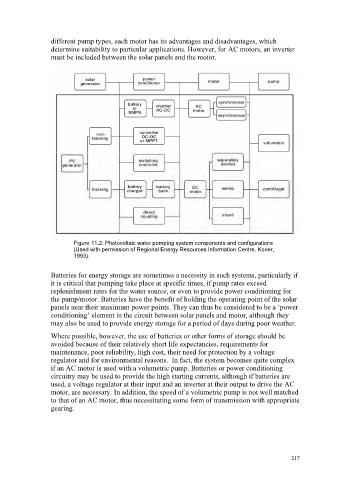
Figure 11.2. Photovoltaic water pumping system components and configurations
(Used with permission of Regional Energy Resources Information Centre, Koner,
1993).
Batteries for energy storage are sometimes a necessity in such systems, particularly if
it is critical that pumping take place at specific times, if pump rates exceed
replenishment rates for the water source, or even to provide power conditioning for
the pump/motor. Batteries have the benefit of holding the operating point of the solar
panels near their maximum power points. They can thus be considered to be a ‘power
conditioning’ element in the circuit between solar panels and motor, although they
may also be used to provide energy storage for a period of days during poor weather.
Where possible, however, the use of batteries or other forms of storage should be
avoided because of their relatively short life expectancies, requirements for
maintenance, poor reliability, high cost, their need for protection by a voltage
regulator and for environmental reasons. In fact, the system becomes quite complex
if an AC motor is used with a volumetric pump. Batteries or power conditioning
circuitry may be used to provide the high starting currents, although if batteries are
used, a voltage regulator at their input and an inverter at their output to drive the AC
motor, are necessary. In addition, the speed of a volumetric pump is not well matched
to that of an AC motor, thus necessitating some form of transmission with appropriate
gearing.
217