Page 131 - Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants Volume I
P. 131
118 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
(text continued from page 115) Flow of gases and vapors (compressible fluids) through
q = cu ft/sec at flowing conditions (Figure 2-37) Coef- nozzles and orifices. (For flow field importance see Refer-
ficient from Reference [22] for liquids discharge ences [31]). From [3]:
r, = critical pressure ratio for compressible flow, =
P',/P'l
q = YC'A , cu ft/sec
(at flowing conditions ) (2-48)
Y = net expansion factor from Figures 2-38A or 2-38B
AP = differential pressure (equal to inlet gauge pressure when
discharging to atmosphere)
p = weight density of fluid, lbs/cu ft at flowing conditions
A = cross section of orifice or nozzle, sq ft
C' = flow coefficient from Figures 2-38A or 2-38B
or, W = 1891 Yd,'C' E, lbs/hr (2-95)
where do = internal diameter of orifice, in
= specific volume of fluid, cu ft/lb
AP Pl
or, q'= ll.3OYd0'C'
at 14.7 psia and 600F (2-96)
where S, = Sp Gr gas relative to air, = mol wt. gas/29
T1 = absolute temperature, "R
P'1 = pressure, psi abs
k = CPj'C~
P' = psia Procedure
B = ratio small-to-large diameter in orifices and nozzles, A. How to determine pipe size for given capacity and pressure
and contractions or enlargements in pipes
drop.
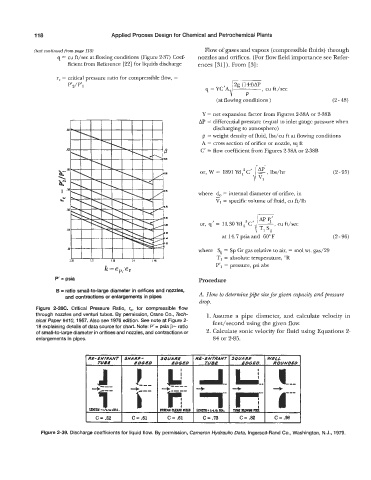
Figure 2-38C. Critical Pressure Ratio, r,, for compressible flow
through nozzles and venturi tubes. By permission, Crane Co., Tech- 1. Assume a pipe diameter, and calculate velocity in
nical Paper #NO, 1957. Also see 1976 edition. See note at Figure 2- feet/second using the given flow.
18 explaining details of data source for chart. Note: P' = psia p= ratio
+:zr , dDGED TUB€ BDGED ROUND€O
of small-to-large diameter in orifices and nozzles, and contractions or 2. Calculate sonic velocity for fluid using Equations 2-
4i-- +ip;- +I' +m- ,---
enlargements in pipes. 84 or 2-85.
M-INtffANr SUARP- 54UAR€ R€- €NTRANT SQUARE W€LL
TU8i
ED&?D
J ! --- U-l--I..C-- ----
*~lrt.iDtA. mu(cuulmnIs mtm*++bm. l~ummnna +
C = .52 C = .61 C = .61 c = .73 C = .82 C=.M