Page 55 -
P. 55
Assemble tasks
After the estimation meeting is finished, the project manager works with the moderator to
gather all of the results from the individual preparation and the estimation session. The
project manager removes redundancies and resolves remaining estimate differences to
generate a final task list, with effort estimates attached to each task. The assumptions are
then summarized and added to the list.
The final task list should be in the same format as the individual preparation results (see
Figure 3-1). In addition, the project manager should create a spreadsheet that lists the
final estimates that each person came up with. The spreadsheet should indicate the best-
case and worst-case scenarios, and it should indicate any place that further discussion will
be required. Any task with an especially wide discrepancy should be marked for further
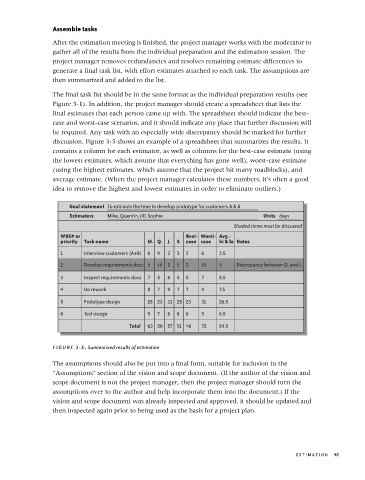
discussion. Figure 3-5 shows an example of a spreadsheet that summarizes the results. It
contains a column for each estimator, as well as columns for the best-case estimate (using
the lowest estimates, which assume that everything has gone well), worst-case estimate
(using the highest estimates, which assume that the project hit many roadblocks), and
average estimate. (When the project manager calculates these numbers, it’s often a good
idea to remove the highest and lowest estimates in order to eliminate outliers.)
Goal statement To estimate the time to develop prototype for customers A & B
Estimators Mike, Quentin, Jill, Sophie Units days
Shaded items must be discussed
WBS# or Best- Worst- Avg.-
priority Task name M. Q. J. S. case case hi & lo Notes
1 Interview customers (A+B) 6 4 3 3 3 6 3.5
2 Develop requirements docs 5 10 2 5 2 10 5 Discrepancy between Q. and J.
3 Inspect requirements docs 7 5 6 5 5 7 5.5
4 Do rework 8 7 9 7 7 9 7.5
5 Prototype design 28 23 31 25 23 31 26.5
6 Test design 9 7 6 6 6 9 6.5
Total 63 56 57 51 46 72 54.5
FIGURE 3-5. Summarized results of estimation
The assumptions should also be put into a final form, suitable for inclusion in the
“Assumptions” section of the vision and scope document. (If the author of the vision and
scope document is not the project manager, then the project manager should turn the
assumptions over to the author and help incorporate them into the document.) If the
vision and scope document was already inspected and approved, it should be updated and
then inspected again prior to being used as the basis for a project plan.
ESTIMATION 47