Page 296 - Artificial Intelligence for the Internet of Everything
P. 296
274 Artificial Intelligence for the Internet of Everything
Message passing: Systems under test
coordination
synchronization
Agent GUI App
Coordinator Agent API SOA
Initiate tests
Collect results
Agent Web
App
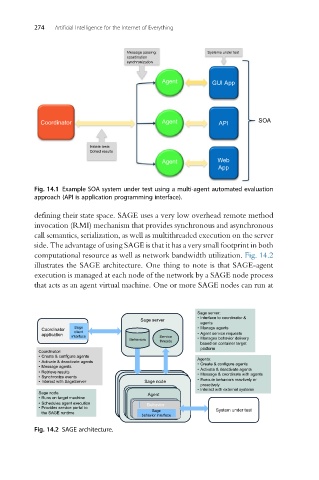
Fig. 14.1 Example SOA system under test using a multi-agent automated evaluation
approach (API is application programming interface).
defining their state space. SAGE uses a very low overhead remote method
invocation (RMI) mechanism that provides synchronous and asynchronous
call semantics, serialization, as well as multithreaded execution on the server
side. The advantage of using SAGE is that it has a very small footprint in both
computational resource as well as network bandwidth utilization. Fig. 14.2
illustrates the SAGE architecture. One thing to note is that SAGE-agent
execution is managed at each node of the network by a SAGE node process
that acts as an agent virtual machine. One or more SAGE nodes can run at
Sage server:
• Interface to coordinator &
Sage server
agents
Coordinator Sage • Manage agents
client
application interface Service • Agent service requests
Behaviors threads • Manages behavior delivery
based on container target
platform
Coordinator:
• Create & configure agents
• Activate & deactivate agents Agents:
Create & configure agents
•
• Message agents
• Retrieve results • • Activate & deactivate agents
Message & coordinate with agents
• Synchronize events • Execute behaviors reavtively or
• Interact with SageServer Sage node
proactively
• Interact with external systems
Sage node: Agent
• Runs on target machine
• Schedules agent execution Behavior
• Provides service portal to
Sage System under test
the SAGE runtime
behavior interface
Fig. 14.2 SAGE architecture.