Page 89 - Artificial Intelligence for the Internet of Everything
P. 89
Active Inference in Multiagent Systems 75
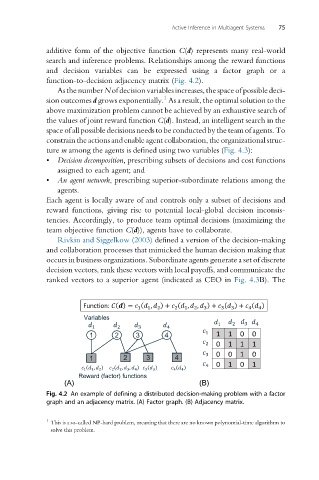
additive form of the objective function C(d) represents many real-world
search and inference problems. Relationships among the reward functions
and decision variables can be expressed using a factor graph or a
function-to-decision adjacency matrix (Fig. 4.2).
AsthenumberN ofdecision variablesincreases,thespaceof possibledeci-
1
sion outcomes d grows exponentially. As a result, the optimal solution to the
above maximization problem cannot be achieved by an exhaustive search of
the values of joint reward function C(d). Instead, an intelligent search in the
space of all possible decisions needs to be conducted by the team of agents. To
constrain the actions and enable agent collaboration, the organizational struc-
ture m among the agents is defined using two variables (Fig. 4.3):
• Decision decomposition, prescribing subsets of decisions and cost functions
assigned to each agent; and
• An agent network, prescribing superior-subordinate relations among the
agents.
Each agent is locally aware of and controls only a subset of decisions and
reward functions, giving rise to potential local-global decision inconsis-
tencies. Accordingly, to produce team optimal decisions (maximizing the
team objective function C(d)), agents have to collaborate.
Rivkin and Siggelkow (2003) defined a version of the decision-making
and collaboration processes that mimicked the human decision making that
occurs in business organizations. Subordinate agents generate a set of discrete
decision vectors, rank these vectors with local payoffs, and communicate the
ranked vectors to a superior agent (indicated as CEO in Fig. 4.3B). The
Variables
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
Reward (factor) functions
(A) (B)
Fig. 4.2 An example of defining a distributed decision-making problem with a factor
graph and an adjacency matrix. (A) Factor graph. (B) Adjacency matrix.
1
This is a so-called NP-hard problem, meaning that there are no known polynomial-time algorithms to
solve this problem.