Page 251 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 251
2
Engine systems 235
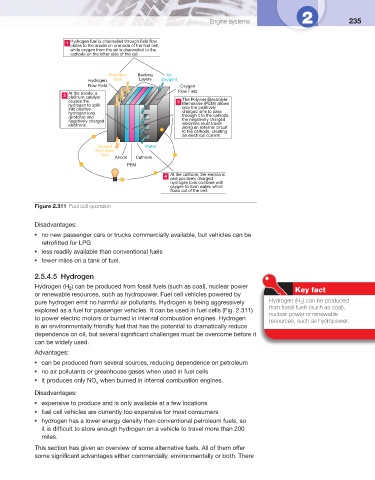
Hydrogen fuel is channelled through field flow
1
plates to the anode on one side of the fuel cell,
while oxygen from the air is channelled to the
cathode on the other side of the cell.
Hydrogen Backing Air
Hydrogen Gas Layers (oxygen)
Flow Field Oxygen
Flow Field
At the anode, a
2
platinum catalyst The Polymer Electrolyte
causes the 3
hydrogen to split Membrane (PEM) allows
only the positively
into positive
hydrogen ions charged ions to pass
through it to the cathode.
(protons) and
negatively charged the negatively charged
electrons must travel
electrons.
– along an external circuit
to the cathode, creating
– an electrical current.
Unused Water
Hydrogen
Gas –
Anode Cathode
– PEM
– At the cathode, the electrons
4
– and positively charged
hydrogen ions combine with
oxygen to form water, which
flows out of the cell.
Figure 2.311 Fuel cell operation
Disadvantages:
no new passenger cars or trucks commercially available, but vehicles can be
●
retrofi tted for LPG
less readily available than conventional fuels
●
fewer miles on a tank of fuel.
●
2.5.4.5 Hydrogen
Hydrogen (H ) can be produced from fossil fuels (such as coal), nuclear power Key fact
2
or renewable resources, such as hydropower. Fuel cell vehicles powered by
pure hydrogen emit no harmful air pollutants. Hydrogen is being aggressively Hydrogen (H 2 ) can be produced
from fossil fuels (such as coal),
explored as a fuel for passenger vehicles. It can be used in fuel cells ( Fig. 2.311 )
nuclear power or renewable
to power electric motors or burned in internal combustion engines. Hydrogen
resources, such as hydropower.
is an environmentally friendly fuel that has the potential to dramatically reduce
dependence on oil, but several signifi cant challenges must be overcome before it
can be widely used.
Advantages:
can be produced from several sources, reducing dependence on petroleum
●
no air pollutants or greenhouse gases when used in fuel cells
●
it produces only NO when burned in internal combustion engines.
●
x
Disadvantages:
expensive to produce and is only available at a few locations
●
fuel cell vehicles are currently too expensive for most consumers
●
hydrogen has a lower energy density than conventional petroleum fuels, so
●
it is diffi cult to store enough hydrogen on a vehicle to travel more than 200
miles.
This section has given an overview of some alternative fuels. All of them offer
some signifi cant advantages either commercially, environmentally or both. There