Page 33 - Basic physical chemistry for the atmospheric sciences
P. 33
Chemical thermodynamics 1 9
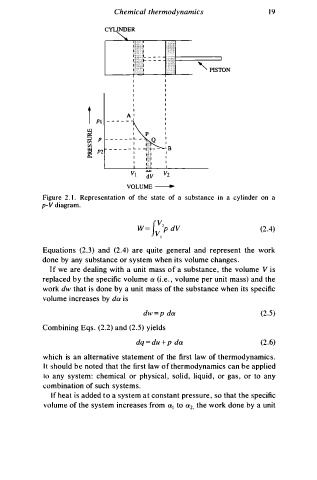
CYLINDER
' P ISTON
t I I
A I
I PI - �: p
-
-
-
-
rll - - - - - 1-- I - . Q
� p -
f/
� P2 - - - - - L I - -(• - - I B
j
J
�
i l
t l
dV
VOLUME -
Figure 2 . I . Representation of the state of a substance in a cylinder on a
p-V diagram.
(2.4)
Equations (2.3) and (2.4) are quite general and represent the work
done by any substance or system when its volume change .
s
I f we are dealing with a unit mass f a substance, the volume V s
i
o
b
e
replaced y the specific volume a (i. . , volume per unit mass) and the
work dw that is done by a unit mass of the substance when its specific
volume increases by da is
dw = p da (2.5)
Combining Eqs. (2.2) and (2.5) yields
dq = d u + p d a (2.6)
which is an alternative statement of the first law of thermodynami s .
c
b
I t should e noted that the first law f thermodynamics can e applied
o
b
lo any system: chemical or physical, solid, liquid, or gas, or to any
i..:ombination of such systems.
If heat is added to a system at constant pressure, so that the specific
volume of the system increases from a1 to a2• the work done by a unit