Page 94 - Basics of MATLAB and Beyond
P. 94
>> v6
v6 =
1 2 3 4 5 6
The feval Function
The feval command is like eval, except that it is used for evaluating
named functions. An example would be:
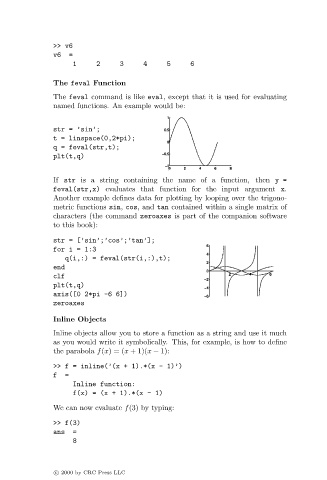
str = ’sin’;
t = linspace(0,2*pi);
q = feval(str,t);
plt(t,q)
If str is a string containing the name of a function, then y=
feval(str,x) evaluates that function for the input argument x.
Another example defines data for plotting by looping over the trigono-
metric functions sin, cos, and tan contained within a single matrix of
characters (the command zeroaxes is part of the companion software
to this book):
str = [’sin’;’cos’;’tan’];
for i = 1:3
q(i,:) = feval(str(i,:),t);
end
clf
plt(t,q)
axis([0 2*pi -6 6])
zeroaxes
Inline Objects
Inline objects allow you to store a function as a string and use it much
as you would write it symbolically. This, for example, is how to define
the parabola f(x)=(x + 1)(x − 1):
>> f = inline(’(x + 1).*(x - 1)’)
f =
Inline function:
f(x) = (x + 1).*(x - 1)
We can now evaluate f(3) by typing:
>> f(3)
ans =
8
c 2000 by CRC Press LLC