Page 57 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 57
38 ChupterFiwe
BUF and NOT Functions
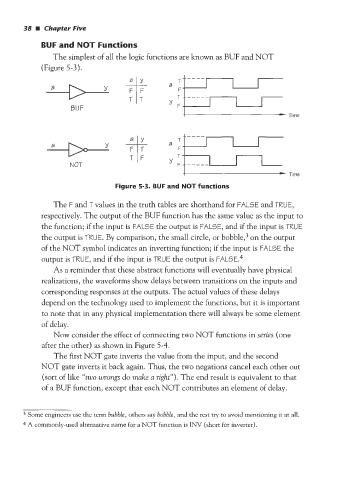
The simplest of all the logic functions are known as BUF and NOT
(Figure 5-3).
BUF
i - Time
a
F T I
NOT F
Figure 5-3. BUF and NOT functions
The F and T values in the truth tables are shorthand for FALSE and TRUE,
respectively. The output of the BUF function has the same value as the input to
the function; if the input is FAL5E the output is FAL5E, and if the input is TRUE
on
the output is TRUE. By comparison, the small circle, or b~bble,~ the output
of the NOT symbol indicates an inverting function; if the input is FALSE the
output is TRUE, and if the input is TRUE the output is FAL5E.‘
As a reminder that these abstract functions will eventually have physical
realizations, the waveforms show delays between transitions on the inputs and
corresponding responses at the outputs. The actual values of these delays
depend on the technology used to implement the functions, but it is important
to note that in any physical implementation there will always be some element
of delay.
Now consider the effect of connecting two NOT functions in series (one
after the other) as shown in Figure 5-4.
The first NOT gate inverts the value from the input, and the second
NOT gate inverts it back again. Thus, the two negations cancel each other out
(sort of like (‘two wrongs do make u right”). The end result is equivalent to that
of a BUF hnction, except that each NOT contributes an element of delay.
3 Some engineers use the term bubble, others say bobble, and the rest try to avoid mentioning it at all.
4 A commonly-used alternative name for a NOT function is INV (short for inverter).