Page 63 - Biorefinery 2030 Future Prospects for the Bioeconomy (2015)
P. 63
1 The Concept of Biorefinery 31
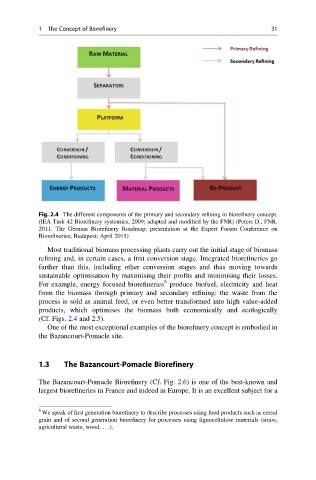
Fig. 2.4 The different components of the primary and secondary refining in biorefinery concept.
(IEA Task 42 Biorefinery systemics, 2009; adapted and modified by the FNR) (Peters D., FNR,
2011. The German Biorefinery Roadmap; presentation at the Expert Forum Conference on
Biorefineries; Budapest; April 2011)
Most traditional biomass processing plants carry out the initial stage of biomass
refining and, in certain cases, a first conversion stage. Integrated biorefineries go
further than this, including other conversion stages and thus moving towards
sustainable optimisation by maximising their profits and minimising their losses.
8
For example, energy focused biorefineries produce biofuel, electricity and heat
from the biomass through primary and secondary refining: the waste from the
process is sold as animal feed, or even better transformed into high value-added
products, which optimises the biomass both economically and ecologically
(Cf. Figs. 2.4 and 2.5).
One of the most exceptional examples of the biorefinery concept is embodied in
the Bazancourt-Pomacle site.
1.3 The Bazancourt-Pomacle Biorefinery
The Bazancourt-Pomacle Biorefinery (Cf. Fig. 2.6) is one of the best-known and
largest biorefineries in France and indeed in Europe. It is an excellent subject for a
8
We speak of first generation biorefinery to describe processes using food products such as cereal
grain and of second generation biorefinery for processes using lignocellulose materials (straw,
agricultural waste, wood, .. .).