Page 152 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 152
Models for Heat Transfer in Heated Substrates 131
Temperature measurement in a soil subject
to temperature variations
Boundary
Objectives Solution of the heat-conduction equation
conditions
Variation of
Exact Environmental Artificial
thermal
measurement
properties
Heat pulse
Understanding
Single probe Dual probe
Solution Expressions
methods used
Analytical Numerical Combination Explicit Implicit
Harmonic Finite Finite
analysis difference elements
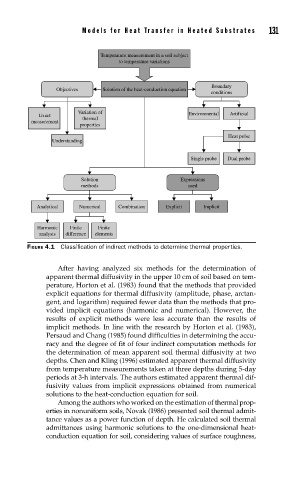
FIGURE 4.1 Classifi cation of indirect methods to determine thermal properties.
After having analyzed six methods for the determination of
apparent thermal diffusivity in the upper 10 cm of soil based on tem-
perature, Horton et al. (1983) found that the methods that provided
explicit equations for thermal diffusivity (amplitude, phase, arctan-
gent, and logarithm) required fewer data than the methods that pro-
vided implicit equations (harmonic and numerical). However, the
results of explicit methods were less accurate than the results of
implicit methods. In line with the research by Horton et al. (1983),
Persaud and Chang (1985) found difficulties in determining the accu-
racy and the degree of fit of four indirect computation methods for
the determination of mean apparent soil thermal diffusivity at two
depths. Chen and Kling (1996) estimated apparent thermal diffusivity
from temperature measurements taken at three depths during 5-day
periods at 3-h intervals. The authors estimated apparent thermal dif-
fusivity values from implicit expressions obtained from numerical
solutions to the heat-conduction equation for soil.
Among the authors who worked on the estimation of thermal prop-
erties in nonuniform soils, Novak (1986) presented soil thermal admit-
tance values as a power function of depth. He calculated soil thermal
admittances using harmonic solutions to the one-dimensional heat-
conduction equation for soil, considering values of surface roughness,