Page 508 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 508
480 Cha pte r Se v e ntee n
Plot the strength of concentration versus absorbance on semilog
paper. Take distilled water as the standard solution.
Extracting and Determining Boron Soil sample (25 g), 50 mL of water, and
0.5 g of activated charcoal are boiled for 5 min in a quartz flask and
filtered immediately through a Whatman No. 42 paper. Pour 5 mL of
extract in 25-mL volumetric flask and add 4 mL of buffer solution, 4 mL
of azomethine–H reagent solution, and make the volume 25 mL with
distilled water. Allow the color to develop for 1 h. The color intensity
is measured spectrophotometrically at 420 nm. By comparing the
measured absorbance to that for the standard curve, we can calculate
the unknown concentration.
Calculation Boron (ppm) in soil sample = concentration of boron in
analyzed sample = reading from the standard curve × 10.
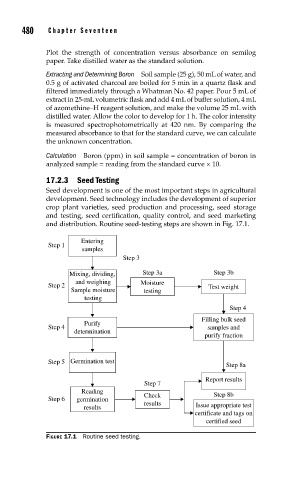
17.2.3 Seed Testing
Seed development is one of the most important steps in agricultural
development. Seed technology includes the development of superior
crop plant varieties, seed production and processing, seed storage
and testing, seed certification, quality control, and seed marketing
and distribution. Routine seed-testing steps are shown in Fig. 17.1.
Entering
Step 1
samples
Step 3
Mixing, dividing, Step 3a Step 3b
and weighing Moisture
Step 2 Test weight
Sample moisture testing
testing
Step 4
Filling bulk seed
Purify
Step 4 samples and
determination
purify fraction
Step 5 Germination test
Step 8a
Report results
Step 7
Reading Step 8b
Step 6 germination Check
results
results Issue appropriate test
certificate and tags on
certified seed
FIGURE 17.1 Routine seed testing.