Page 522 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 522
494 Cha pte r Se v e ntee n
Epigeic (manure worm) Lives in and consumes decomposable
organic matter, is small in size, and
is uniformly pigmented, suitable for
vermicomposting
Species: Eisenia foetida
Endogeic (subsoil dweller) Small to large in size, weekly pigmented,
lives in burrows in organic mineral
complex of soil, consumes soil
Species: Apporrectodea caliginosa,
Octolasion cyaneum
Anecic (topsoil dweller) Large in size, has brown pigment
anteriorly and dorsally, lives in a deep
vertical burrow in soil, casting on surface
Species: Lumbricus terrestris,
Allolobophora longa
In a tropical climate, endogeic and anecic earthworms dominate
the epigeic species. The species most commonly used for vermicom-
posting is Eisenia foetida. It can thrive well under a wide range of tem-
peratures, 4 to 30°C and moisture of about 60 to 30 percent, and can
live in organic matter in a wider pH range, from 6 to 8.
Earthworms feed on any organic waste; however, the acceptabil-
ity and palatability of the waste depends on the texture as well as the
chemical nature of the food material. Earthworms swallow the food
material, which passes through the alimentary canal equipped with a
minigrinder gizzard. After consumption, the organic matter must
have undergone physical and chemical breakdown through the activ-
ity of the muscular gizzard, which grinds the material to a particle
size of 1 to 2 μm. Usually, under ideal conditions, earthworms consume
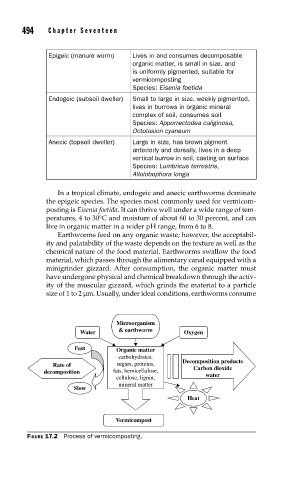
Microorganism
Water & earthworm Oxygen
Fast Organic matter
carbohydrates,
Decomposition products
Rate of sugars, proteins, Carbon dioxide
decomposition fats, hemicellulose, water
cellulose, lignin,
mineral matter
Slow
Heat
Vermicompost
FIGURE 17.2 Process of vermicomposting.