Page 107 - Bridge and Highway Structure Rehabilitation and Repair
P. 107
82 SECTION 1 ADMINISTRATIVE ISSUES
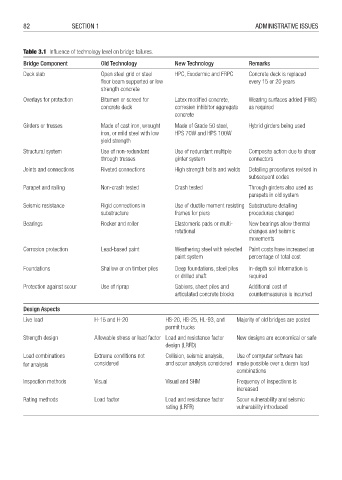
Table 3.1 Infl uence of technology level on bridge failures.
Bridge Component Old Technology New Technology Remarks
Deck slab Open steel grid or steel HPC, Exodermic and FRPC Concrete deck is replaced
fl oor beam supported or low every 15 or 20 years
strength concrete
Overlays for protection Bitumen or screed for Latex modifi ed concrete, Wearing surfaces added (FWS)
concrete deck corrosion inhibitor aggregate as required
concrete
Girders or trusses Made of cast iron, wrought Made of Grade 50 steel, Hybrid girders being used
iron, or mild steel with low HPS 70W and HPS 100W
yield strength
Structural system Use of non-redundant Use of redundant multiple Composite action due to shear
through trusses girder system connectors
Joints and connections Riveted connections High strength bolts and welds Detailing procedures revised in
subsequent codes
Parapet and railing Non-crash tested Crash tested Through girders also used as
parapets in old system
Seismic resistance Rigid connections in Use of ductile moment resisting Substructure detailing
substructure frames for piers procedures changed
Bearings Rocker and roller Elastomeric pads or multi- New bearings allow thermal
rotational changes and seismic
movements
Corrosion protection Lead-based paint Weathering steel with selected Paint costs have increased as
paint system percentage of total cost
Foundations Shallow or on timber piles Deep foundations, steel piles In-depth soil information is
or drilled shaft required
Protection against scour Use of riprap Gabions, sheet piles and Additional cost of
articulated concrete blocks countermeasures is incurred
Design Aspects
Live load H-15 and H-20 HS-20, HS-25, HL-93, and Majority of old bridges are posted
permit trucks
Strength design Allowable stress or load factor Load and resistance factor New designs are economical or safe
design (LRFD)
Load combinations Extreme conditions not Collision, seismic analysis, Use of computer software has
for analysis considered and scour analysis considered made possible over a dozen load
combinations
Inspection methods Visual Visual and SHM Frequency of inspections is
increased
Rating methods Load factor Load and resistance factor Scour vulnerability and seismic
rating (LRFR) vulnerability introduced