Page 94 - Build Your Own Combat Robot
P. 94
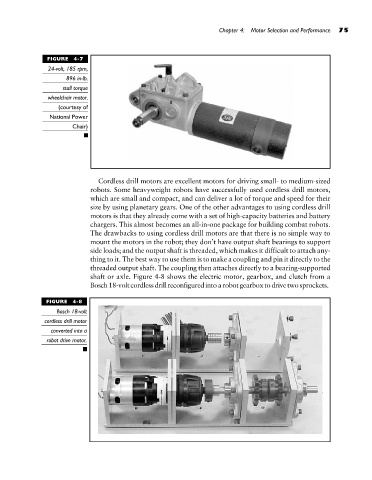
FIGURE 4-7 Chapter 4: Motor Selection and Performance 75
24-volt, 185 rpm,
896 in-lb.
stall torque
wheelchair motor.
(courtesy of
National Power
Chair)
Cordless drill motors are excellent motors for driving small- to medium-sized
robots. Some heavyweight robots have successfully used cordless drill motors,
which are small and compact, and can deliver a lot of torque and speed for their
size by using planetary gears. One of the other advantages to using cordless drill
motors is that they already come with a set of high-capacity batteries and battery
chargers. This almost becomes an all-in-one package for building combat robots.
The drawbacks to using cordless drill motors are that there is no simple way to
mount the motors in the robot; they don’t have output shaft bearings to support
side loads; and the output shaft is threaded, which makes it difficult to attach any-
thing to it. The best way to use them is to make a coupling and pin it directly to the
threaded output shaft. The coupling then attaches directly to a bearing-supported
shaft or axle. Figure 4-8 shows the electric motor, gearbox, and clutch from a
Bosch18-voltcordlessdrillreconfiguredintoarobotgearboxtodrivetwosprockets.
FIGURE 4-8
Bosch 18-volt
cordless drill motor
converted into a
robot drive motor.