Page 30 - Building Big Data Applications
P. 30
24 Building Big Data Applications
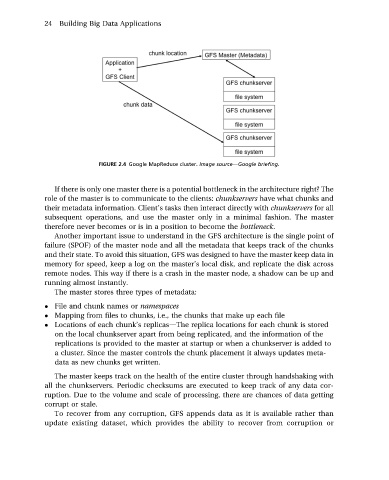
FIGURE 2.4 Google MapReduce cluster. Image sourcedGoogle briefing.
If there is only one master there is a potential bottleneck in the architecture right? The
role of the master is to communicate to the clients: chunkservers have what chunks and
their metadata information. Client’s tasks then interact directly with chunkservers for all
subsequent operations, and use the master only in a minimal fashion. The master
therefore never becomes or is in a position to become the bottleneck.
Another important issue to understand in the GFS architecture is the single point of
failure (SPOF) of the master node and all the metadata that keeps track of the chunks
and their state. To avoid this situation, GFS was designed to have the master keep data in
memory for speed, keep a log on the master’s local disk, and replicate the disk across
remote nodes. This way if there is a crash in the master node, a shadow can be up and
running almost instantly.
The master stores three types of metadata:
File and chunk names or namespaces
Mapping from files to chunks, i.e., the chunks that make up each file
Locations of each chunk’s replicasdThe replica locations for each chunk is stored
on the local chunkserver apart from being replicated, and the information of the
replications is provided to the master at startup or when a chunkserver is added to
a cluster. Since the master controls the chunk placement it always updates meta-
data as new chunks get written.
The master keeps track on the health of the entire cluster through handshaking with
all the chunkservers. Periodic checksums are executed to keep track of any data cor-
ruption. Due to the volume and scale of processing, there are chances of data getting
corrupt or stale.
To recover from any corruption, GFS appends data as it is available rather than
update existing dataset, which provides the ability to recover from corruption or