Page 72 - Building Big Data Applications
P. 72
66 Building Big Data Applications
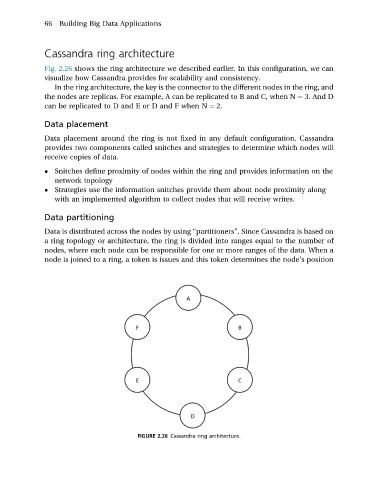
Cassandra ring architecture
Fig. 2.26 shows the ring architecture we described earlier. In this configuration, we can
visualize how Cassandra provides for scalability and consistency.
In the ring architecture, the key is the connector to the different nodes in the ring, and
the nodes are replicas. For example, A can be replicated to B and C, when N ¼ 3. And D
can be replicated to D and E or D and F when N ¼ 2.
Data placement
Data placement around the ring is not fixed in any default configuration. Cassandra
provides two components called snitches and strategies to determine which nodes will
receive copies of data.
Snitches define proximity of nodes within the ring and provides information on the
network topology
Strategies use the information snitches provide them about node proximity along
with an implemented algorithm to collect nodes that will receive writes.
Data partitioning
Data is distributed across the nodes by using “partitioners”. Since Cassandra is based on
a ring topology or architecture, the ring is divided into ranges equal to the number of
nodes, where each node can be responsible for one or more ranges of the data. When a
node is joined to a ring, a token is issues and this token determines the node’s position
FIGURE 2.26 Cassandra ring architecture.