Page 42 - Calculus Workbook For Dummies
P. 42
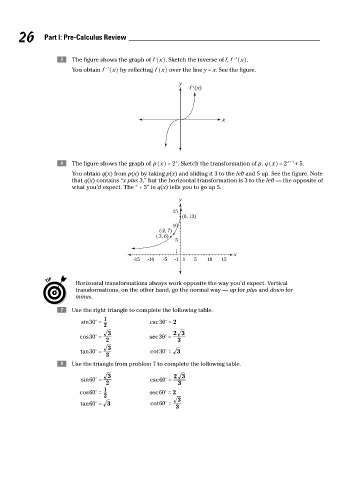
26 Part I: Pre-Calculus Review
-
1
e The figure shows the graph of f xh. Sketch the inverse of f, f ^ h.
x
^
1
-
x
You obtain f ^ h by reflecting f xh over the line y = x. See the figure.
^
y
f (x)
-1
x
x
f The figure shows the graph of p x = 2 . Sketch the transformation of p, q x = 2 x + 3 + 5.
^ h
^ h
You obtain q(x) from p(x) by taking p(x) and sliding it 3 to the left and 5 up. See the figure. Note
that q(x) contains “x plus 3,” but the horizontal transformation is 3 to the left — the opposite of
what you’d expect. The “ + 5” in q(x) tells you to go up 5.
y
15
(0, 13)
10
(-2, 7)
(-3, 6)
5
1
x
-15 -10 -5 -1 1 5 10 15
Horizontal transformations always work opposite the way you’d expect. Vertical
transformations, on the other hand, go the normal way — up for plus and down for
minus.
g Use the right triangle to complete the following table.
1
sin30c = csc30c = 2
2
3 2 3
cos30c = sec30c =
2 3
3
tan30c = cot30c = 3
3
h Use the triangle from problem 7 to complete the following table.
3 2 3
sin60c = csc60c =
2 3
1
cos60c = sec60c = 2
2
3
tan60c = 3 cot60c =
3