Page 237 - Caldera Volcanism Analysis, Modelling and Response
P. 237
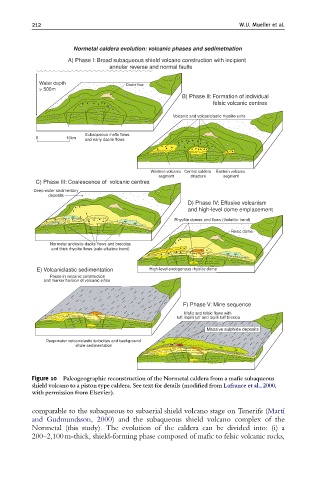
212 W.U. Mueller et al.
Normetal caldera evolution: volcanic phases and sedimetnation
A) Phase I: Broad subaqueous shield volcano construction with incipient
annular reverse and normal faults
Water depth Dacite flow
> 500m
B) Phase II: Formation of individual
felsic volcanic centres
Volcanic and volcaniclastic rhyolite units
Subaqueous mafic flows
0 10km and early dacite flows
Western volcanic Central caldera Eastern volcanic
segment structure segment
C) Phase III: Coalescence of volcanic centres
Deep-water sedimentary
deposits
D) Phase IV: Effusive volcanism
and high-level dome emplacement
Rhyolite domes and flows (tholeiitic trend)
Felsic dome
Normetal andesite-dacite flows and breccias
and thick rhyolite flows (calc-alkaline trend)
E) Volcaniclastic sedimentation High-level endogenous rhyolite dome
Pause in volcanic construction
and marker horizon of volcanic eifice
F) Phase V: Mine sequence
Mafic and felsic flows with
tuff, lapilli tuff and lapilli tuff breccia
Massive sulphide deposits
Deep-water volcaniclastic turbidites and background
shale sedimentation
Figure 10 Paleogeographic reconstruction of the Normetal caldera from a ma¢c subaqueous
shield volcano to a piston type caldera. See text for details (modi¢ed from Lafrance et al., 2000,
with permission from Elsevier).
comparable to the subaqueous to subaerial shield volcano stage on Tenerife (Martı ´
and Gudmundsson, 2000) and the subaqueous shield volcano complex of the
Normetal (this study). The evolution of the caldera can be divided into: (i) a
200–2,100 m-thick, shield-forming phase composed of mafic to felsic volcanic rocks,