Page 382 - Caldera Volcanism Analysis, Modelling and Response
P. 382
Facilitating Dike Intrusions into Ring-Faults 357
Deflating spherical magma reservoir
A) Map view, model setup B) Map view, displacement vectors
Magma chamber 20
(10 MPa pressure drop)
10
5 X X'
0 Subsidence
Subsidence
Subsidence
5 km radius
y
Cross-section
-10
in x-direction
x -20
-20 -10 0 10 20 -20 -10 0 10 20
)
C) Cross-section, x-displacement (U x
0
X X'
-10
-20
)
D) Cross-section, z-displacement (U z [in m]
0
X X' 1
-10 0
-20 -1
-20 -10 0 10 20
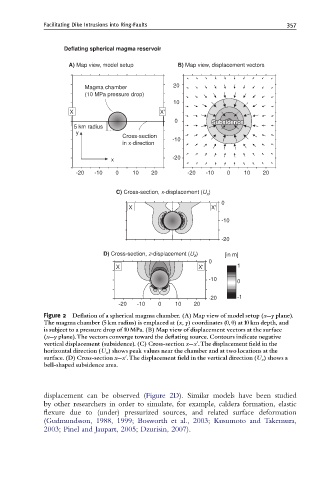
Figure 2 De£ation of a spherical magma chamber. (A) Map view of model setup (x--y plane).
The magma chamber (5 km radius) is emplaced at (x, y) coordinates (0, 0) at 10 km depth, and
is subject to a pressure drop of 10 MPa. (B) Map view of displacement vectors at the surface
(x--y plane).The vectors converge toward the de£ating source. Contours indicate negative
vertical displacement (subsidence). (C) Cross-section x--xu.The displacement ¢eld in the
horizontal direction (U x ) shows peak values near the chamber and at two locations at the
surface. (D) Cross-section x--xu.The displacement ¢eld in the vertical direction (U z ) shows a
bell-shaped subsidence area.
displacement can be observed (Figure 2D). Similar models have been studied
by other researchers in order to simulate, for example, caldera formation, elastic
flexure due to (under) pressurized sources, and related surface deformation
(Gudmundsson, 1988, 1999; Bosworth et al., 2003; Kusumoto and Takemura,
2003; Pinel and Jaupart, 2005; Dzurisin, 2007).