Page 266 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 266
256 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
Metal filament CNT yarn Metal filament –600
CNT
CNT yarn –500 Pt+CNT
Au+CNT
AuAg+CNT
–400 Ag+CNT
Z" (ohm) –300 Cu+CNT
PtCu+CNT
PVA-H 3 PO 4 coating
–200
Electrode 2 Electrode 1
–100
PVA-H 3 PO 4 coating
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 1000 2000 3000
Multi-ply yarn supercapacitor Z' (ohm)
(A) (B)
1.5
100
80 Cu+CNT 1.0
Current density (A/g) 40 1.0 V Potential (V) 0.5 Cu+CNT
60
1.2 V
1.0 V
1.4 V
20
1.2 V
1.4 V
–20 0
0.0
–40
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 0 5 10 15 20 25 30
(C) Potential (V) (D) Time (S)
70
80
60
50 Cu+CNT Cu+CNT
Capacitance (F/g) 40 Energy density (Wh/kg) 60
40
30
20
10 20
0 0
1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 0 50000 100000 150000
(E) Potential (V) (F) Power density (W/kg)
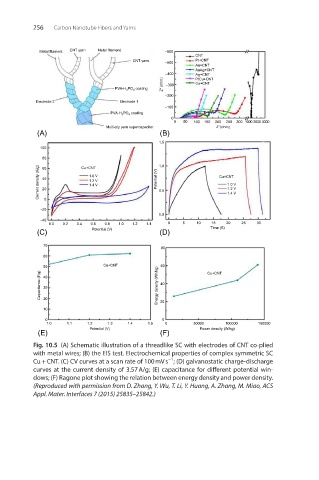
Fig. 10.5 (A) Schematic illustration of a threadlike SC with electrodes of CNT co-plied
with metal wires; (B) the EIS test. Electrochemical properties of complex symmetric SC
−1
Cu + CNT. (C) CV curves at a scan rate of 100 mV s ; (D) galvanostatic charge-discharge
curves at the current density of 3.57 A/g; (E) capacitance for different potential win-
dows; (F) Ragone plot showing the relation between energy density and power density.
(Reproduced with permission from D. Zhang, Y. Wu, T. Li, Y. Huang, A. Zhang, M. Miao, ACS
Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 (2015) 25835–25842.)