Page 17 - Carbonate Platforms Facies, Sequences, and Evolution
P. 17
to
east
now
1986a;
The
the
energy
1990a).
prevailed
ocyathids
laminated
found
indicates
and
over
Trucial
margin,
Gandin,
a
and barite lenses.
Laminated
trapped
with
Coast
in
top of the sabkha complex
stromatolitic
1990a).
consisting of early dolomite
climate transition: Laminated
Dolomite/Ceroide Limestone
evaporitic
limestone intraclasts and calcite
Epiphyton,
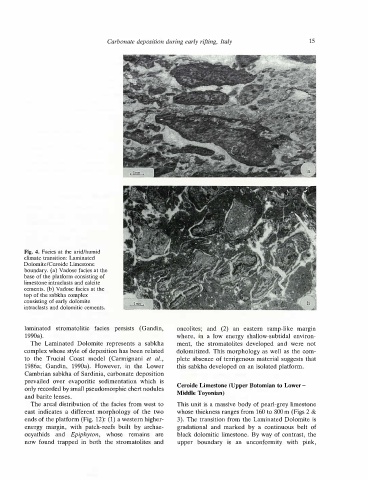
Fig. 4. Facies at the arid/humid
both
Dolomite
cements. (b) Vadose facies at the
base of the platform consisting of
intraclasts and dolomitic cements.
model
boundary. (a) Vadose facies at the
facies
the
patch-reefs
However,
whose
in
built
persists
represents
sedimentation
different morphology of
a
by
the
(Carmignani
remains
et
the
stromatolites
which
archae
ends of the platform (Fig. 12): (1) a western higher
(Gandin,
al.,
and
The areal distribution of the facies from west to
two
are
complex whose style of deposition has been related
only recorded by small pseudomorphic chert nodules
Cambrian sabkha of Sardinia, carbonate deposition
Lower
is
sabkha
ment,
upper
where,
oncolites;
in
the
gradational
a
dolomitized.
and
Carbonate deposition during early rifting,
and
boundary
low
Middle Toyonian)
(2)
is
Italy
an
an
stromatolites
energy
marked
black dolomitic limestone.
by
a
eastern
developed
unconformity
and
shallow-subtidal
ramp-like
continuous
with
this sabkha developed on an isolated platform.
were
Ceroide Limestone (Upper Botomian to Lower
belt
environ
This morphology as well as the com
15
margin
pink,
whose thickness ranges from 160 to 800 m (Figs 2 &
By way of contrast, the
plete absence of terrigenous material suggests that
not
This unit is a massive body of pearl-grey limestone
of
3). The transition from the Laminated Dolomite is