Page 176 - Carbonate Platforms Facies, Sequences, and Evolution
P. 176
8
the
162
The
rapid
Kendall
interior.
decrease
shows
easy
building.
discussed
&
the
the
Thus,
sediment
margin of Monte
removal
depositional
Schlager
of
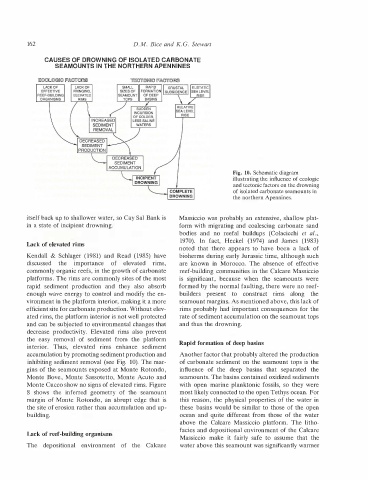
Lack of elevated rims
inferred
productivity.
elevated
(1981)
production
importance
rims
sediment
Lack of reef-building organisms
in a state of incipient drowning.
Elevated
and
and
environment
geometry
of
of
inhibiting sediment removal (see Fig.
of
from
rims
they
Read
the
enhance
the
the
also
also
elevated
(1985)
10). The mar
efficient site for carbonate production. Without elev
enough wave energy to control and modify the en
the site of erosion rather than accumulation and up
platforms. The rims are commonly sites of the most
commonly organic reefs, in the growth of carbonate
rims,
sediment
have
itself back up to shallower water, so Cay Sal Bank is
and can be subjected to environmental changes that
vironment in the platform interior, making it a more
ated rims, the platform interior is not well protected
Monte Bove, Monte Sassotetto, Monte Acuto and
absorb
accumulation by promoting sediment production and
platform
Monte Cucco show no signs of elevated rims. Figure
prevent
gins of the seamounts exposed at Monte Rotondo,
Rotondo, an abrupt edge that is
seamount
Calcare
is
are
D.M. Bice and K.G.
SEAMOUNTS IN THE NORTHERN APENNINES
with
these
1970).
noted
above
bodies
CAUSES OF DROWNING OF ISOLATED CARBONATE
builders
influence
Massiccio
In
the
open
that
known
and
Stewart
of
significant,
in
no
fact,
make
the
there
present
Calcare
it
to
reefal
because
and thus the drowning.
deep
Heckel
Morocco.
fairly
appears to
when
Massiccio
The
basins
safe
Rapid formation of deep basins
(1974)
buildups
construct
the
to
have
that
and
marine planktonic fossils,
ocean and quite different from those
rims
absence
platform.
been
the northern Apennines.
of
assume
a
Fig. 10. Schematic diagram
James
(Colacicchi
The
seamounts
along
et
separated
that
lack
of isolated carbonate seamounts in
formed by the normal faulting, there were no reef
Massiccio was probably an extensive, shallow plat
litho
and tectonic factors on the drowning
illustrating the influence of ecologic
a/.,
form with migrating and coalescing carbonate sand
rims probably had important consequences for the
the
rate of sediment accumulation on the seamount tops
the
of carbonate sediment on the seamount tops is the
were
bioherms during early Jurassic time, although such
(1983)
effective
reef-building communities in the Calcare Massiccio
this reason, the physical properties of the water in
basins would be similar to those of the open
of the water
water above this seamount was significantly warmer
the
facies and depositional environment of the Calcare
Another factor that probably altered the production
seamount margins. As mentioned above, this lack of
of
most likely connected to the open Tethys ocean. For
so they were
seamounts. The basins contained oxidized sediments