Page 267 - Carbonate Platforms Facies, Sequences, and Evolution
P. 267
the
\....
I
I
faulting
platform.
separates
off
the
El Doctor,
this
Saltillo to Monterrey
��los
Valles
(=
r LAND
of cross-section of Fig. 10.
E-W
Cd.Acuna
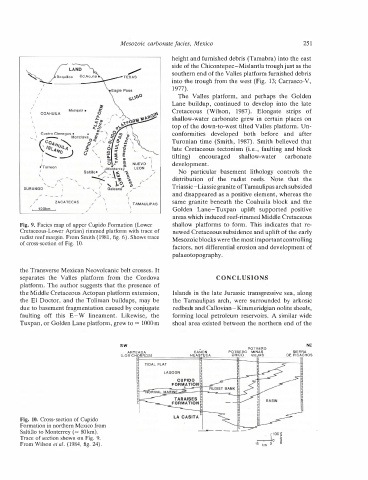
Fig. 10. Cross-section of Cupido
80km).
Trace of section shown on Fig. 9.
From Wilson et al. (1984, fig. 24).
platform
Formation in northern Mexico from
lineament.
from
sw
Tuxpan, or Golden Lane platform, grew to
the
TEXAS
and the Toliman buildups,
,.-/
Mesozoic
ARTEAGA
Likewise,
(LOS CHORROS)
Fig. 9. Facies map of upper Cupido Formation (Lower
Cretaceous-Lower Aptian) rimmed platform with trace of
the Middle Cretaceous Actopan platform extension,
may be
rudist reef margin. From Smith (1981, fig. 6). Shows trace
due to basement fragmentation caused by conjugate
the
Cordova
The author suggests that the presence of
the Transverse Mexican Neovolcanic belt crosses. It
= 1000 m
carbonate
the
Lane
No
The
1977).
tilting)
shallow
Golden
Cretaceous
distribution
conformities
CANON
development.
Valles
HUASTECA
Turonian time
buildup,
of
facies, Mexico
Tamaulipas
particular
platforms
palaeotopography.
the
Lane-Tux
encouraged
arch,
(Wilson,
pan
platform,
developed
continued
CHICO
POTRERO
rudist
basement
to form.
were
to
and
1987).
(Smith, 1987).
uplift
both
15
This
VIEJAS
MINAS
POTRERO
reefs.
km
forming local petroleum reservoirs.
CONCLUSIONS
0
develop
Smith
..---.---+ 0
lithology
perhaps
shallow-water
before
surrounded
E
Elongate
•
r ,oo �
Note
into
supported
the
indicates
and
believed
that
the
controls
strips
same granite beneath the Coahuila block and
that
SIERRA
top of the down-to-west tilted Valles platform. Un
re
side of the Chicontepec-Mislantla trough just as the
late
NE
southern end of the Valles platform furnished debris
into the trough from the west (Fig. 13; Carrasco-V,
height and furnished debris (Tamabra) into the east
Golden
DE PICACHOS
the
positive
Triassic-Liassic granite of Tamaulipas arch subsided
and disappeared as a positive element, whereas the
A similar wide
redbeds and Callovian-Kimmeridgian oolite shoals,
areas which induced reef-rimmed Middle Cretaceous
shoal area existed between the northern end of the
after
that
of
shallow-water carbonate grew in certain places on
the
the
late Cretaceous tectonism (i.e., faulting and block
carbonate
by arkosic
Islands in the late Jurassic transgressive sea, along
factors, not differential erosion and development of
newed Cretaceous subsidence and uplift of the early
Mesozoic blocks were the most important controlling
251