Page 34 - Carbonate Platforms Facies, Sequences, and Evolution
P. 34
(1)
clasts
facies
These
Breccias
of
of
Paleokarsts
are
Ammonitico
laminated
Neptunian dykes
calcite (Fazzuoli et
filled
Massiccio
Rosso
vadose
by
that
silt
the Ammonitico
the
Limestone
(Fig.
al., 1981; Fig.
locally
Rosso.
or
achelles of Lower Sinemurian age.
pink
lla);
llb).
(2)
encloses
Smaller
ammonite
lithofacies
breccias; and (3) pink, laminated or massive litho
lum
Two different types of breccia can be distinguished.
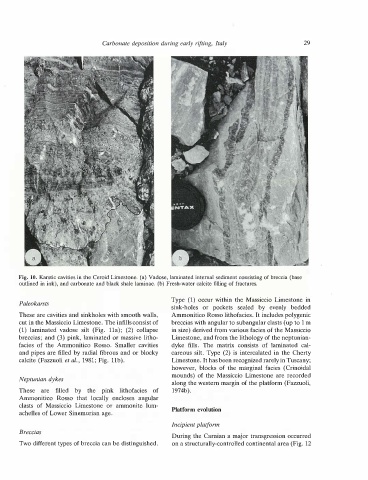
These are cavities and sinkholes with smooth walls,
of
collapse
cut in the Massiccio Limestone. The infills consist of
cavities
and pipes are filled by radial fibrous and or blocky
angular
dyke
1974b).
however,
sink-holes
fills.
mounds) of
careous silt.
or
The
Incipient plat form
Platform evolution
Carbonate deposition during early rifting, Italy
pockets
matrix
sealed
outlined in ink), and carbonate and black shale laminae. (b) Fresh-water calcite filling of fractures.
consists
by
of
blocks of the marginal facies
evenly
laminated
Fig. 10. Karstic cavities in the Ceroid Limestone. (a) Vadose, laminated internal sediment consisting of breccia (base
cal
Limestone, and from the lithology of the neptunian
along the western margin of the platform (Fazzuoli,
29
Type (1) occur within the Massiccio Limestone in
bedded
the Massiccio Limestone are recorded
(Crinoidal
on a structurally-controlled continental area (Fig. 12
During the Carnian a major transgression occurred
Limestone. It has been recognized rarely in Tuscany;
Ammonitico Rosso lithofacies. It includes polygenic
in size) derived from various facies of the Massiccio
Type (2) is intercalated in the Cherty
breccias with angular to subangular clasts (up to 1m