Page 71 - Carbonate Platforms Facies, Sequences, and Evolution
P. 71
facies
imental
Francis,
Walther
Objectives
can
magnitude.
calculations
cyclothemic
thickness of
THE
was
to
that forms the
give
1983),
program
each
but
those
any
patterns
and sedimentation rates.
that
in
of
basis for
principally
are
PROGRAM
3· 5cm kyr- 1 sedimentation rate.
reliable
late
cyclothem is
Leeder
introduces
modelling.
developed
extremely
( op
equal
as
indication
Dinantian
cit)
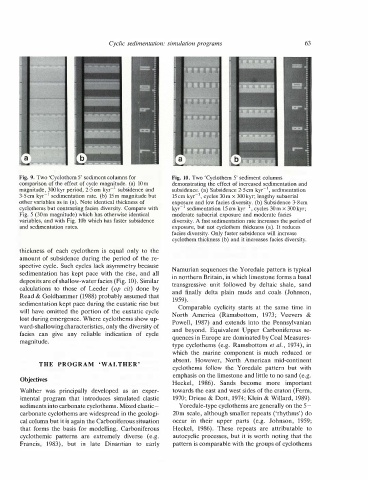
comparison of the effect of cycle magnitude. (a)
Fig. 9. Two 'Cyclothem 5' sediment columns for
only
an
'WALTHER'
simulated
of
to
diverse
other variables as in (a). Note identical thickness of
to
10 m
done
Fig. 5 (30m magnitude) which has otherwise identical
magnitude, 300 kyr period, 2· 5 em kyr- 1 subsidence and
variables, and with Fig. lOb which has faster subsidence
(b) 15m magnitude but
sediments into carbonate cyclothems. Mixed clastic
amount of subsidence during the period of the re
lost during emergence. Where cyclothems show up
exper
carbonate cyclothems are widespread in the geologi
cyclothems but contrasting facies diversity. Compare with
cycle
sedimentation has kept pace with the rise, and all
deposits are of shallow-water facies (Fig. 10). Similar
Carboniferous
the
ward-shallowing characteristics, only the diversity of
spective cycle. Such cycles lack asymmetry because
cal column but it is again the Carboniferous situation
will have omitted the portion of the eustatic cycle
(e.g.
by
Read & Goldhammer (1988) probably assumed that
clastic
sedimentation kept pace during the eustatic rise but
early
and
and
occur
North
1959).
which
absent.
Powell,
Heckel,
Heckel,
in
the
cyclothems
finally
beyond.
transgressive
Comparable
their
1986).
1986).
America
delta
unit
marine
Cyclic sedimentation: simulation programs
However,
follow
kyr- 1 sedimentation 15
type cyclothems (e.g.
upper
These
the
plain
cyclicity
Sands
Fig. 10. Two 'Cyclothem 5'
Equivalent
North
followed
em kyr-
parts
muds
starts
component
repeats
by
(Ramsbottom,
is
at
become
Yoredale
and
(e.g.
are
American
the
deltaic
1973;
much
more
coals
sediment columns
pattern
same
moderate subaerial exposure and moderate facies
Johnson,
shale,
facies diversity. Only faster subsidence will increase
but
15cm kyr- 1 , cycles 30 m x 300 kyr; lengthy subaerial
exposure, but not cyclothem thickness (a). It reduces
Upper Carboniferous
Veevers
reduced
attributable
time
, cycles 30 m x 300 kyr;
subsidence. (a) Subsidence 2·5 em kyr- 1 , sedimentation
cyclothem thickness (b) and it increases facies diversity.
demonstrating the effect of increased sedimentation and
exposure and low facies diversiti" (b) Subsidence 3·8 em
quences in Europe are dominated by Coal Measures
se
Yoredale-type cyclothems are generally on the 5-
1970; Driese & Dott, 1974; Klein & Willard, 1989).
emphasis on the limestone and little to no sand (e.g.
(Johnson,
63
Namurian sequences the Yoredale pattern is typical
with
Ramsbottom et al., 1974), in
1987) and extends into the Pennsylvanian
&
sand
diversity. A fast sedimentation rate increases the period of
in northern Britain, in which limestone forms a basal
1959;
20m scale, although smaller repeats ('rhythms') do
or
autocyclic processes, but it is worth noting that the
in
mid-continent
to
towards the east and west sides of the craton (Ferm,
important
pattern is comparable with the groups of cyclothems