Page 78 - Centrifugal Pumps Design and Application
P. 78
Volute Design 61
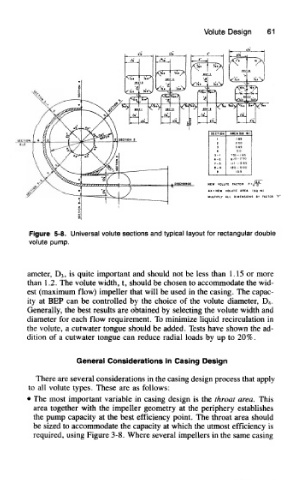
Figure 5-8. Universal volute sections and typical layout for rectangular double
volute pump.
ameter, D 3, is quite important and should not be less than 1.15 or more
than 1.2. The volute width, t, should be chosen to accommodate the wid-
est (maximum flow) impeller that will be used in the casing. The capac-
ity at BEP can be controlled by the choice of the volute diameter, D 4.
Generally, the best results are obtained by selecting the volute width and
diameter for each flow requirement. To minimize liquid recirculation in
the volute, a cutwater tongue should be added. Tests have shown the ad-
dition of a cutwater tongue can reduce radial loads by up to 20%.
General Considerations in Casing Design
There are several considerations in the casing design process that apply
to all volute types. These are as follows:
• The most important variable in casing design is the throat area. This
area together with the impeller geometry at the periphery establishes
the pump capacity at the best efficiency point. The throat area should
be sized to accommodate the capacity at which the utmost efficiency is
required, using Figure 3-8. Where several impellers in the same casing