Page 119 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 119
DATA COLLECTION AND ECONOMIC ANALYSIS 97
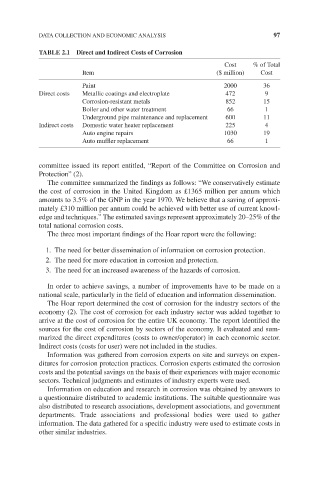
TABLE 2.1 Direct and Indirect Costs of Corrosion
Cost %ofTotal
Item ($ million) Cost
Paint 2000 36
Direct costs Metallic coatings and electroplate 472 9
Corrosion-resistant metals 852 15
Boiler and other water treatment 66 1
Underground pipe maintenance and replacement 600 11
Indirect costs Domestic water heater replacement 225 4
Auto engine repairs 1030 19
Auto muffler replacement 66 1
committee issued its report entitled, “Report of the Committee on Corrosion and
Protection” (2).
The committee summarized the findings as follows: “We conservatively estimate
the cost of corrosion in the United Kingdom as £1365 million per annum which
amounts to 3.5% of the GNP in the year 1970. We believe that a saving of approxi-
mately £310 million per annum could be achieved with better use of current knowl-
edge and techniques.” The estimated savings represent approximately 20–25% of the
total national corrosion costs.
The three most important findings of the Hoar report were the following:
1. The need for better dissemination of information on corrosion protection.
2. The need for more education in corrosion and protection.
3. The need for an increased awareness of the hazards of corrosion.
In order to achieve savings, a number of improvements have to be made on a
national scale, particularly in the field of education and information dissemination.
The Hoar report determined the cost of corrosion for the industry sectors of the
economy (2). The cost of corrosion for each industry sector was added together to
arrive at the cost of corrosion for the entire UK economy. The report identified the
sources for the cost of corrosion by sectors of the economy. It evaluated and sum-
marized the direct expenditures (costs to owner/operator) in each economic sector.
Indirect costs (costs for user) were not included in the studies.
Information was gathered from corrosion experts on site and surveys on expen-
ditures for corrosion protection practices. Corrosion experts estimated the corrosion
costs and the potential savings on the basis of their experiences with major economic
sectors. Technical judgments and estimates of industry experts were used.
Information on education and research in corrosion was obtained by answers to
a questionnaire distributed to academic institutions. The suitable questionnaire was
also distributed to research associations, development associations, and government
departments. Trade associations and professional bodies were used to gather
information. The data gathered for a specific industry were used to estimate costs in
other similar industries.