Page 191 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 191
HAZARDOUS MATERIALS TRANSPORT 169
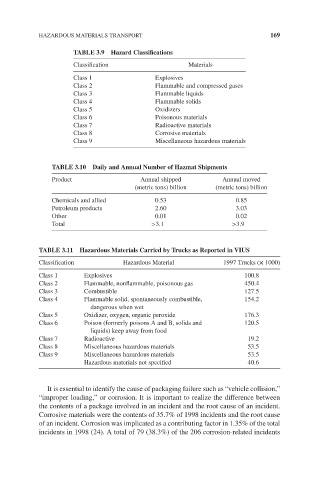
TABLE 3.9 Hazard Classifications
Classification Materials
Class 1 Explosives
Class 2 Flammable and compressed gases
Class 3 Flammable liquids
Class 4 Flammable solids
Class 5 Oxidizers
Class 6 Poisonous materials
Class 7 Radioactive materials
Class 8 Corrosive materials
Class 9 Miscellaneous hazardous materials
TABLE 3.10 Daily and Annual Number of Hazmat Shipments
Product Annual shipped Annual moved
(metric tons) billion (metric tons) billion
Chemicals and allied 0.53 0.85
Petroleum products 2.60 3.03
Other 0.01 0.02
Total >3.1 >3.9
TABLE 3.11 Hazardous Materials Carried by Trucks as Reported in VIUS
Classification Hazardous Material 1997 Trucks (× 1000)
Class 1 Explosives 100.8
Class 2 Flammable, nonflammable, poisonous gas 450.4
Class 3 Combustible 127.5
Class 4 Flammable solid, spontaneously combustible, 154.2
dangerous when wet
Class 5 Oxidizer, oxygen, organic peroxide 176.3
Class 6 Poison (formerly poisons A and B, solids and 120.5
liquids) keep away from food
Class 7 Radioactive 19.2
Class 8 Miscellaneous hazardous materials 53.5
Class 9 Miscellaneous hazardous materials 53.5
Hazardous materials not specified 40.6
It is essential to identify the cause of packaging failure such as “vehicle collision,”
“improper loading,” or corrosion. It is important to realize the difference between
the contents of a package involved in an incident and the root cause of an incident.
Corrosive materials were the contents of 35.7% of 1998 incidents and the root cause
of an incident. Corrosion was implicated as a contributing factor in 1.35% of the total
incidents in 1998 (24). A total of 79 (38.3%) of the 206 corrosion-related incidents