Page 159 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 159
Speight_Part II_B 11/7/01 3:11 PM Page 2.100
2.100 MANUFACTURE OF CHEMICALS
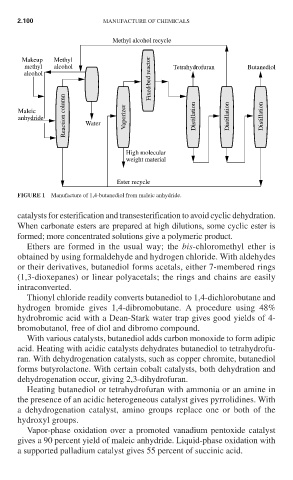
Methyl alcohol recycle
Makeup Methyl
methyl alcohol Tetrahydrofuran Butanediol
alcohol Fixed-bed reactor
Reaction column
Maleic
anhydride Water Vaporizer Distillation Distillation Distillation
High molecular
weight material
Ester recycle
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of 1,4-butanediol from maleic anhydride.
catalysts for esterification and transesterification to avoid cyclic dehydration.
When carbonate esters are prepared at high dilutions, some cyclic ester is
formed; more concentrated solutions give a polymeric product.
Ethers are formed in the usual way; the bis-chloromethyl ether is
obtained by using formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride. With aldehydes
or their derivatives, butanediol forms acetals, either 7-membered rings
(1,3-dioxepanes) or linear polyacetals; the rings and chains are easily
intraconverted.
Thionyl chloride readily converts butanediol to 1,4-dichlorobutane and
hydrogen bromide gives 1,4-dibromobutane. A procedure using 48%
hydrobromic acid with a Dean-Stark water trap gives good yields of 4-
bromobutanol, free of diol and dibromo compound.
With various catalysts, butanediol adds carbon monoxide to form adipic
acid. Heating with acidic catalysts dehydrates butanediol to tetrahydrofu-
ran. With dehydrogenation catalysts, such as copper chromite, butanediol
forms butyrolactone. With certain cobalt catalysts, both dehydration and
dehydrogenation occur, giving 2,3-dihydrofuran.
Heating butanediol or tetrahydrofuran with ammonia or an amine in
the presence of an acidic heterogeneous catalyst gives pyrrolidines. With
a dehydrogenation catalyst, amino groups replace one or both of the
hydroxyl groups.
Vapor-phase oxidation over a promoted vanadium pentoxide catalyst
gives a 90 percent yield of maleic anhydride. Liquid-phase oxidation with
a supported palladium catalyst gives 55 percent of succinic acid.