Page 359 - Chemical engineering design
P. 359
334
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
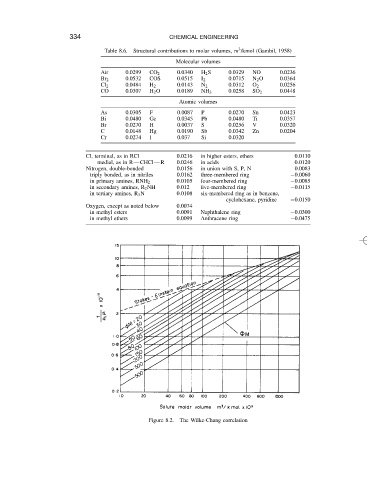
Table 8.6.
Structural contributions to molar volumes, m /kmol (Gambil, 1958)
Molecular volumes 3
Air 0.0299 CO 2 0.0340 H 2 S 0.0329 NO 0.0236
Br 2 0.0532 COS 0.0515 I 2 0.0715 N 2 O 0.0364
Cl 2 0.0484 H 2 0.0143 N 2 0.0312 O 2 0.0256
CO 0.0307 H 2 O 0.0189 NH 3 0.0258 SO 2 0.0448
Atomic volumes
As 0.0305 F 0.0087 P 0.0270 Sn 0.0423
Bi 0.0480 Ge 0.0345 Pb 0.0480 Ti 0.0357
Br 0.0270 H 0.0037 S 0.0256 V 0.0320
C 0.0148 Hg 0.0190 Sb 0.0342 Zn 0.0204
Cr 0.0274 I 0.037 Si 0.0320
Cl, terminal, as in RCl 0.0216 in higher esters, ethers 0.0110
medial, as in R CHCl R 0.0246 in acids 0.0120
Nitrogen, double-bonded 0.0156 in union with S, P, N 0.0083
triply bonded, as in nitriles 0.0162 three-membered ring 0.0060
in primary amines, RNH 2 0.0105 four-membered ring 0.0085
in secondary amines, R 2 NH 0.012 five-membered ring 0.0115
in tertiary amines, R 3 N 0.0108 six-membered ring as in benzene,
cyclohexane, pyridine 0.0150
Oxygen, except as noted below 0.0074
in methyl esters 0.0091 Naphthalene ring 0.0300
in methyl ethers 0.0099 Anthracene ring 0.0475
Figure 8.2. The Wilke-Chang correlation