Page 376 - Chemical engineering design
P. 376
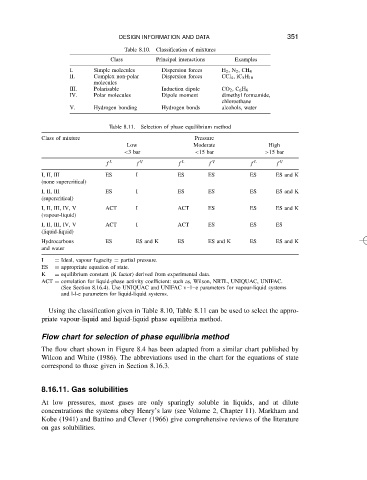
DESIGN INFORMATION AND DATA
Principal interactions
Class Table 8.10. Classification of mixtures Examples 351
I. Simple molecules Dispersion forces H 2 ,N 2 ,CH 4
II. Complex non-polar Dispersion forces CCl 4 ,iC 5 H 10
molecules
III. Polarisable Induction dipole CO 2 ,C 6 H 6
IV. Polar molecules Dipole moment dimethyl formamide,
chloroethane
V. Hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonds alcohols, water
Table 8.11. Selection of phase equilibrium method
Class of mixture Pressure
Low Moderate High
<3bar <15 bar >15 bar
f L f V f L f V f L f V
I, II, III ES I ES ES ES ES and K
(none supercritical)
I, II, III ES I ES ES ES ES and K
(supercritical)
I, II, III, IV, V ACT I ACT ES ES ES and K
(vapour-liquid)
I, II, III, IV, V ACT I ACT ES ES ES
(liquid-liquid)
Hydrocarbons ES ES and K ES ES and K ES ES and K
and water
I D Ideal, vapour fugacity D partial pressure.
ES D appropriate equation of state.
K D equilibrium constant (K factor) derived from experimental data.
ACT D correlation for liquid-phase activity coefficient: such as, Wilson, NRTL, UNIQUAC, UNIFAC.
(See Section 8.16.4). Use UNIQUAC and UNIFAC v l e parameters for vapour-liquid systems
and l-l-e parameters for liquid-liquid systems.
Using the classification given in Table 8.10, Table 8.11 can be used to select the appro-
priate vapour-liquid and liquid-liquid phase equilibria method.
Flow chart for selection of phase equilibria method
The flow chart shown in Figure 8.4 has been adapted from a similar chart published by
Wilcon and White (1986). The abbreviations used in the chart for the equations of state
correspond to those given in Section 8.16.3.
8.16.11. Gas solubilities
At low pressures, most gases are only sparingly soluble in liquids, and at dilute
concentrations the systems obey Henry’s law (see Volume 2, Chapter 11). Markham and
Kobe (1941) and Battino and Clever (1966) give comprehensive reviews of the literature
on gas solubilities.