Page 134 - Compact Numerical Methods For Computers
P. 134
Real symmetric matrices 123
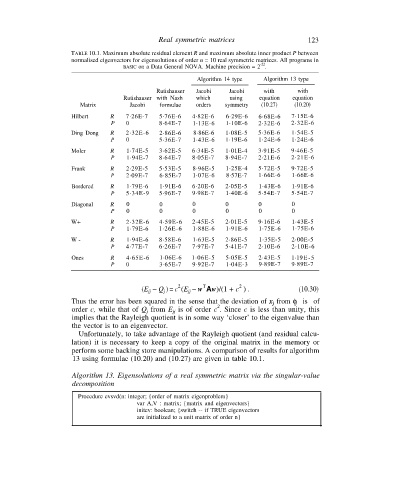
TABLE 10.1. Maximum absolute residual element R and maximum absolute inner product P between
normalised eigenvectors for eigensolutions of order n = 10 real symmetric matrices. All programs in
-22
BASIC on a Data General NOVA. Machine precision = 2 .
Algorithm 14 type Algorithm 13 type
Rutishauser Jacobi Jacobi with with
Rutishauser with Nash which using equation equation
Matrix Jacobi formulae orders symmetry (10.27) (10.20)
Hilbert R 7·26E-7 5·76E-6 4·82E-6 6·29E-6 6·68E-6 7·15E-6
P 0 8·64E-7 1·13E-6 1·10E-6 2·32E-6 2·32E-6
Ding Dong R 2·32E-6 2·86E-6 8·86E-6 1·08E-5 5·36E-6 1·54E-5
P 0 5·36E-7 1·43E-6 1·19E-6 1·24E-6 1·24E-6
Moler R 1·74E-5 3·62E-5 6·34E-5 1·01E-4 3·91E-5 9·46E-5
P 1·94E-7 8·64E-7 8·05E-7 8·94E-7 2·21E-6 2·21E-6
Frank R 2·29E-5 5·53E-5 8·96E-5 1·25E-4 5·72E-5 9·72E-5
P 2·09E-7 6·85E-7 1·07E-6 8·57E-7 1·66E-6 1·66E-6
Bordered R 1·79E-6 1·91E-6 6·20E-6 2·05E-5 1·43E-6 1·91E-6
P 5·34E-9 5·96E-7 9·98E-7 1·40E-6 5·54E-7 5·54E-7
Diagonal R 0 0 0 0 0 0
P 0 0 0 0 0 0
W+ R 2·32E-6 4·59E-6 2·45E-5 2·01E-5 9·16E-6 1·43E-5
P 1·79E-6 1·26E-6 1·88E-6 1·91E-6 1·75E-6 1·75E-6
W - R 1·94E-6 8·58E-6 1·63E-5 2·86E-5 1·35E-5 2·00E-5
P 4·77E-7 6·26E-7 7·97E-7 5·41E-7 2·10E-6 2·10E-6
Ones R 4·65E-6 1·06E-6 1·06E-5 5·05E-5 2·43E-5 l·l9E-5
P 0 3·65E-7 9·92E-7 1·04E-3 9·89E-7 9·89E-7
2 T 2
(E – Q ) = c (E – w Aw)/(1 + c ) . (10.30)
jj j jj
f
Thus the error has been squared in the sense that the deviation of x j from f j is of
2
order c, while that of Q j from E jj is of order c . Since c is less than unity, this
implies that the Rayleigh quotient is in some way ‘closer’ to the eigenvalue than
the vector is to an eigenvector.
Unfortunately, to take advantage of the Rayleigh quotient (and residual calcu-
lation) it is necessary to keep a copy of the original matrix in the memory or
perform some backing store manipulations. A comparison of results for algorithm
13 using formulae (10.20) and (10.27) are given in table 10.1.
Algorithm 13. Eigensolutions of a real symmetric matrix via the singular-value
decomposition
Procedure evsvd(n: integer; {order of matrix eigenproblem}
var A,V : matrix; {matrix and eigenvectors}
initev: boolean; {switch -- if TRUE eigenvectors
are initialized to a unit matrix of order n}