Page 189 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 189
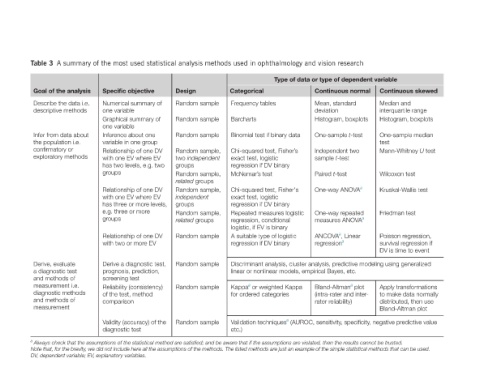
Continuous skewed Median and interquartile range Histogram, boxplots One-sample median test Mann-Whitney U test Wilcoxon test Kruskal-Wallis test Friedman test Poisson regression, survival regression if DV is time to event Apply transformations to make data normally distributed, then use Bland-Altman plot
Type of data or type of dependent variable Continuous normal Mean, standard deviation Histogram, boxplots One-sample t-test Independent two sample t-test Paired t-test One-way ANOVA a One-way repeated measures ANOVA a ANCOVA a , Linear regression a Discriminant analysis, cluster analysis, predictive modeling using generalized linear or nonlinear models, empirical Bayes, etc. Bland-Altma
Table 3 A summary of the most used statistical analysis methods used in ophthalmology and vision research
Categorical Frequency tables Barcharts Binomial test if binary data Chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test, logistic regression if DV binary McNemar’s test Chi-squared test, Fisher's exact test, logistic regression if DV binary Repeated measures logistic regression, conditional logistic, if EV is binary A suitable type of logistic regression if DV binary Kappa a or weighted Kappa
Random sample Random sample Random sample Random sample, two independent Random sample, related groups Random sample, independent Random sample, related groups Random sample Random sample Random sample Random sample a Always check that the assumptions of the statistical method are satisfied; and be aware that if the assumptions are violated, then the results cannot be trusted.
Design groups groups
Specific objective Numerical summary of one variable Graphical summary of one variable Inference about one variable in one group Relationship of one DV with one EV where EV has two levels, e.g. two groups Relationship of one DV with one EV where EV has three or more levels, e.g. three or more groups Relationship of one DV with two or more EV Derive a diagnostic test, progn
Goal of the analysis Describe the data i.e. descriptive methods Infer from data about the population i.e. confirmatory or exploratory methods Derive, evaluate a diagnostic test and methods of measurement i.e. diagnostic methods and methods of measurement DV, dependent variable; EV, explanatory variables.