Page 264 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 264
262 CHAPTER 13 Drusen and macular degeneration
4 Diagnosis of AMD
The development of medical image analysis tools for the diagnosis of AMD has not
been as active as for diabetic retinopathy (DR), largely due to the existence of screen-
ing programs for DR, which do not exist for AMD.
However, extensive work has been done using color fundus images. Since AMD
is characterized by lesions (a.k.a. image features), it would seem natural at first sight
to pursue methods based on lesion segmentation. However, due to the difficulty in
segmenting AMD-related lesions, this is very challenging. The diagnosis of AMD
via color fundus images seem to flourish with image-based methods, which is coin-
cident with the deep learning strategies. For instance, Zheng et al. [86] proposed a
strategy using the quad-tree concept to divide fundus images reclusively until homo-
geneity is met: e.g. intensity-based or other metrics between parent and child regions
being less than a pre-defined threshold. A graph could then be used to represent the
decomposition and graph-mining techniques could be used to produce feature vec-
tors. These derived features can then be used by classification techniques, such as
SVM and Bayesian classifiers, to classify the images. Good performance has been
observed using this approach.
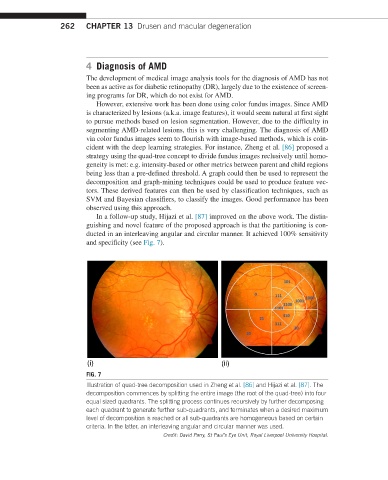
In a follow-up study, Hijazi et al. [87] improved on the above work. The distin-
guishing and novel feature of the proposed approach is that the partitioning is con-
ducted in an interleaving angular and circular manner. It achieved 100% sensitivity
and specificity (see Fig. 7).
(i) (ii)
FIG. 7
Illustration of quad-tree decomposition used in Zheng et al. [86] and Hijazi et al. [87]. The
decomposition commences by splitting the entire image (the root of the quad-tree) into four
equal sized quadrants. The splitting process continues recursively by further decomposing
each quadrant to generate further sub-quadrants, and terminates when a desired maximum
level of decomposition is reached or all sub-quadrants are homogeneous based on certain
criteria. In the latter, an interleaving angular and circular manner was used.
Credit: David Parry, St Paul’s Eye Unit, Royal Liverpool University Hospital.