Page 164 -
P. 164
144 Chapter 5
Source Line: SAP AG.
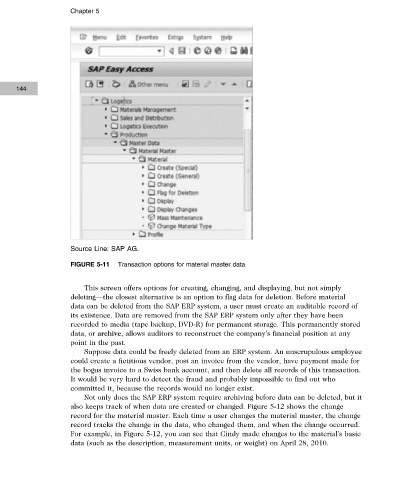
FIGURE 5-11 Transaction options for material master data
This screen offers options for creating, changing, and displaying, but not simply
deleting—the closest alternative is an option to flag data for deletion. Before material
data can be deleted from the SAP ERP system, a user must create an auditable record of
its existence. Data are removed from the SAP ERP system only after they have been
recorded to media (tape backup, DVD-R) for permanent storage. This permanently stored
data, or archive, allows auditors to reconstruct the company’s financial position at any
point in the past.
Suppose data could be freely deleted from an ERP system. An unscrupulous employee
could create a fictitious vendor, post an invoice from the vendor, have payment made for
the bogus invoice to a Swiss bank account, and then delete all records of this transaction.
It would be very hard to detect the fraud and probably impossible to find out who
committed it, because the records would no longer exist.
Not only does the SAP ERP system require archiving before data can be deleted, but it
also keeps track of when data are created or changed. Figure 5-12 shows the change
record for the material master. Each time a user changes the material master, the change
record tracks the change in the data, who changed them, and when the change occurred.
For example, in Figure 5-12, you can see that Cindy made changes to the material’s basic
data (such as the description, measurement units, or weight) on April 28, 2010.
Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.