Page 166 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 166
Industrial Robot
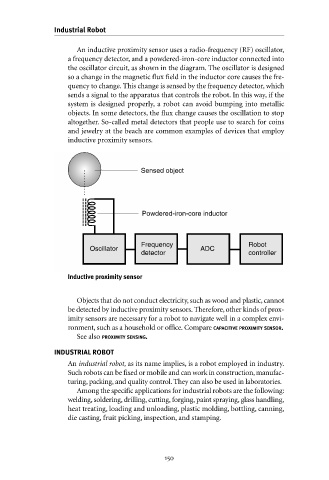
An inductive proximity sensor uses a radio-frequency (RF) oscillator,
a frequency detector, and a powdered-iron-core inductor connected into
the oscillator circuit, as shown in the diagram. The oscillator is designed
so a change in the magnetic flux field in the inductor core causes the fre-
quency to change. This change is sensed by the frequency detector, which
sends a signal to the apparatus that controls the robot. In this way, if the
system is designed properly, a robot can avoid bumping into metallic
objects. In some detectors, the flux change causes the oscillation to stop
altogether. So-called metal detectors that people use to search for coins
and jewelry at the beach are common examples of devices that employ
inductive proximity sensors.
Sensed object
Powdered-iron-core inductor
Frequency Robot
Oscillator ADC
detector controller
Inductive proximity sensor
Objects that do not conduct electricity, such as wood and plastic, cannot
be detected by inductive proximity sensors.Therefore,other kinds of prox-
imity sensors are necessary for a robot to navigate well in a complex envi-
ronment, such as a household or office. Compare CAPACITIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR.
See also PROXIMITY SENSING.
INDUSTRIAL ROBOT
An industrial robot, as its name implies, is a robot employed in industry.
Such robots can be fixed or mobile and can work in construction,manufac-
turing, packing, and quality control. They can also be used in laboratories.
Among the specific applications for industrial robots are the following:
welding, soldering, drilling, cutting, forging, paint spraying, glass handling,
heat treating, loading and unloading, plastic molding, bottling, canning,
die casting, fruit picking, inspection, and stamping.