Page 236 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 236
Parallax
PARALLAX
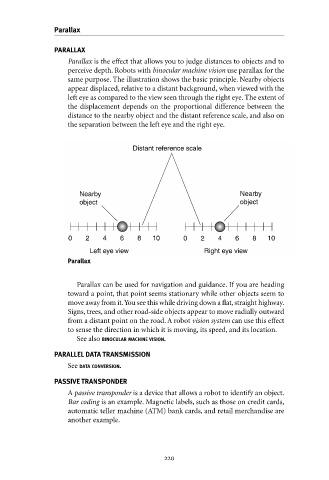
Parallax is the effect that allows you to judge distances to objects and to
perceive depth. Robots with binocular machine vision use parallax for the
same purpose. The illustration shows the basic principle. Nearby objects
appear displaced, relative to a distant background, when viewed with the
left eye as compared to the view seen through the right eye. The extent of
the displacement depends on the proportional difference between the
distance to the nearby object and the distant reference scale, and also on
the separation between the left eye and the right eye.
Distant reference scale
Nearby Nearby
object object
0 2 4 6 8 10 0 2 4 6 8 10
Left eye view Right eye view
Parallax
Parallax can be used for navigation and guidance. If you are heading
toward a point, that point seems stationary while other objects seem to
move away from it.You see this while driving down a flat, straight highway.
Signs, trees, and other road-side objects appear to move radially outward
from a distant point on the road. A robot vision system can use this effect
to sense the direction in which it is moving, its speed, and its location.
See also BINOCULAR MACHINE VISION.
PARALLEL DATA TRANSMISSION
See DATA CONVERSION.
PASSIVE TRANSPONDER
A passive transponder is a device that allows a robot to identify an object.
Bar coding is an example. Magnetic labels, such as those on credit cards,
automatic teller machine (ATM) bank cards, and retail merchandise are
another example.