Page 40 - Construction Waterproofing Handbook
P. 40
2.4 CHAPTER TWO
Prefabricated Drainage System
Installation
The product can be laid into preexisting
trenches available from foundation construction
or trenches constructed specifically for the
drainage field. The width of the trench is typi-
cally 2–6 in wide. The depth of the trench is
determined upon the actual site conditions and
soil permeability. Figure 2.6 represents a typical
drainage detail.
The prefabricated plastic drains usually
permit the excavated soil to be used as back-
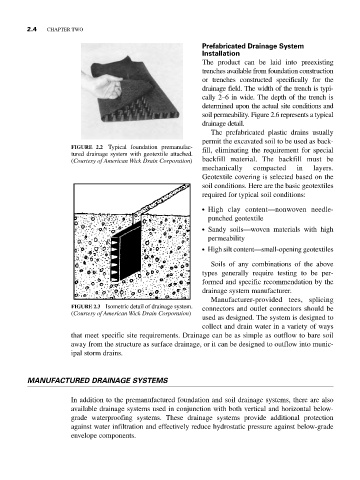
FIGURE 2.2 Typical foundation premanufac- fill, eliminating the requirement for special
tured drainage system with geotextile attached.
(Courtesy of American Wick Drain Corporation) backfill material. The backfill must be
mechanically compacted in layers.
Geotextile covering is selected based on the
soil conditions. Here are the basic geotextiles
required for typical soil conditions:
● High clay content—nonwoven needle-
punched geotextile
● Sandy soils—woven materials with high
permeability
● High silt content—small-opening geotextiles
Soils of any combinations of the above
types generally require testing to be per-
formed and specific recommendation by the
drainage system manufacturer.
Manufacturer-provided tees, splicing
FIGURE 2.3 Isometric detail of drainage system. connectors and outlet connectors should be
(Courtesy of American Wick Drain Corporation)
used as designed. The system is designed to
collect and drain water in a variety of ways
that meet specific site requirements. Drainage can be as simple as outflow to bare soil
away from the structure as surface drainage, or it can be designed to outflow into munic-
ipal storm drains.
MANUFACTURED DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
In addition to the premanufactured foundation and soil drainage systems, there are also
available drainage systems used in conjunction with both vertical and horizontal below-
grade waterproofing systems. These drainage systems provide additional protection
against water infiltration and effectively reduce hydrostatic pressure against below-grade
envelope components.