Page 79 - Coulson Richardson's Chemical Engineering Vol.6 Chemical Engineering Design 4th Edition
P. 79
62
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
often required. A rough estimate can be made by assuming either reversible adiabatic
(isentropic) or isothermal expansion, depending on the nature of the process.
For isothermal expansion (expansion at constant temperature):
Pv D constant
For reversible adiabatic expansion (no heat exchange with the surroundings):
Pv D constant
where D ratio of the specific heats, C p /C v .
The compression and expansion of gases is covered more fully in Section 3.13.
3.3.5. Heat
Energy is transferred either as heat or work. A system does not contain “heat”, but the
transfer of heat or work to a system changes its internal energy.
Heat taken in by a system from its surroundings is conventionally taken as positive
and that given out as negative.
3.3.6. Electrical energy
Electrical, and the mechanical forms of energy, are included in the work term in an energy
balance. Electrical energy will only be significant in energy balances on electrochemical
processes.
3.4. THE ENERGY BALANCE
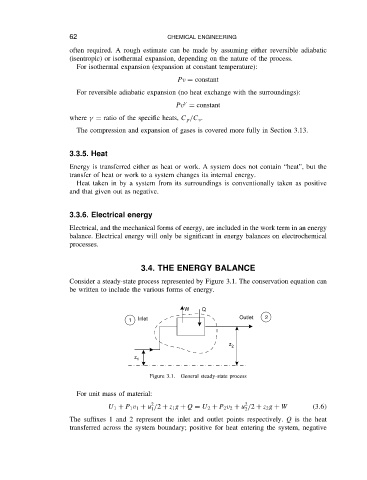
Consider a steady-state process represented by Figure 3.1. The conservation equation can
be written to include the various forms of energy.
W Q
1 Inlet Outlet 2
z
2
z 1
Figure 3.1. General steady-state process
For unit mass of material:
2 2
U 1 C P 1 v 1 C u /2 C z 1 g C Q D U 2 C P 2 v 2 C u /2 C z 2 g C W 3.6
2
1
The suffixes 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet points respectively. Q is the heat
transferred across the system boundary; positive for heat entering the system, negative