Page 306 - Cultures and Organizations
P. 306
Yesterday, Now, or Later? 275
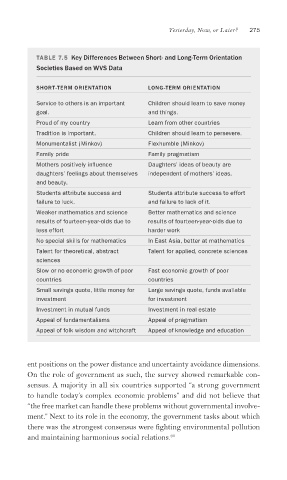
TABLE 7.5 Key Differences Between Short- and Long-Term Orientation
Societies Based on WVS Data
SHORT-TERM ORIENTATION LONG-TERM ORIENTATION
Service to others is an important Children should learn to save money
goal. and things.
Proud of my country Learn from other countries
Tradition is important. Children should learn to persevere.
Monumentalist (Minkov) Flexhumble (Minkov)
Family pride Family pragmatism
Mothers positively infl uence Daughters’ ideas of beauty are
daughters’ feelings about themselves independent of mothers’ ideas.
and beauty.
Students attribute success and Students attribute success to effort
failure to luck. and failure to lack of it.
Weaker mathematics and science Better mathematics and science
results of fourteen-year-olds due to results of fourteen-year-olds due to
less effort harder work
No special skills for mathematics In East Asia, better at mathematics
Talent for theoretical, abstract Talent for applied, concrete sciences
sciences
Slow or no economic growth of poor Fast economic growth of poor
countries countries
Small savings quote, little money for Large savings quote, funds available
investment for investment
Investment in mutual funds Investment in real estate
Appeal of fundamentalisms Appeal of pragmatism
Appeal of folk wisdom and witchcraft Appeal of knowledge and education
ent positions on the power distance and uncertainty avoidance dimensions.
On the role of government as such, the survey showed remarkable con-
sensus. A majority in all six countries supported “a strong government
to handle today’s complex economic problems” and did not believe that
“the free market can handle these problems without governmental involve-
ment.” Next to its role in the economy, the government tasks about which
there was the strongest consensus were fighting environmental pollution
and maintaining harmonious social relations. 91