Page 606 - Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications
P. 606
9.2 n-ary Relations and Their Applications 585
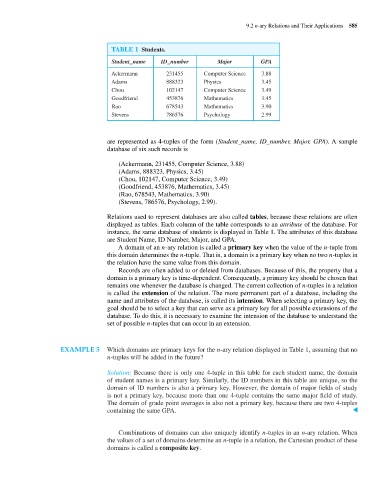
TABLE 1 Students.
Student_name ID_number Major GPA
Ackermann 231455 Computer Science 3.88
Adams 888323 Physics 3.45
Chou 102147 Computer Science 3.49
Goodfriend 453876 Mathematics 3.45
Rao 678543 Mathematics 3.90
Stevens 786576 Psychology 2.99
are represented as 4-tuples of the form (Student_name, ID_number, Major, GPA). A sample
database of six such records is
(Ackermann, 231455, Computer Science, 3.88)
(Adams, 888323, Physics, 3.45)
(Chou, 102147, Computer Science, 3.49)
(Goodfriend, 453876, Mathematics, 3.45)
(Rao, 678543, Mathematics, 3.90)
(Stevens, 786576, Psychology, 2.99).
Relations used to represent databases are also called tables, because these relations are often
displayed as tables. Each column of the table corresponds to an attribute of the database. For
instance, the same database of students is displayed in Table 1. The attributes of this database
are Student Name, ID Number, Major, and GPA.
A domain of an n-ary relation is called a primary key when the value of the n-tuple from
this domain determines the n-tuple. That is, a domain is a primary key when no two n-tuples in
the relation have the same value from this domain.
Records are often added to or deleted from databases. Because of this, the property that a
domain is a primary key is time-dependent. Consequently, a primary key should be chosen that
remains one whenever the database is changed. The current collection of n-tuples in a relation
is called the extension of the relation. The more permanent part of a database, including the
name and attributes of the database, is called its intension. When selecting a primary key, the
goal should be to select a key that can serve as a primary key for all possible extensions of the
database. To do this, it is necessary to examine the intension of the database to understand the
set of possible n-tuples that can occur in an extension.
EXAMPLE 5 Which domains are primary keys for the n-ary relation displayed in Table 1, assuming that no
n-tuples will be added in the future?
Solution: Because there is only one 4-tuple in this table for each student name, the domain
of student names is a primary key. Similarly, the ID numbers in this table are unique, so the
domain of ID numbers is also a primary key. However, the domain of major fields of study
is not a primary key, because more than one 4-tuple contains the same major field of study.
The domain of grade point averages is also not a primary key, because there are two 4-tuples
containing the same GPA. ▲
Combinations of domains can also uniquely identify n-tuples in an n-ary relation. When
the values of a set of domains determine an n-tuple in a relation, the Cartesian product of these
domains is called a composite key.