Page 202 -
P. 202
2011/6/1
11-ch04-125-186-9780123814791
3:17 Page 165
HAN
#41
4.5 Data Warehouse Implementation 165
of detailed data to be stored in a relational database, while aggregations are kept in
a separate MOLAP store. The Microsoft SQL Server 2000 supports a hybrid OLAP
server.
Specialized SQL servers: To meet the growing demand of OLAP processing in rela-
tional databases, some database system vendors implement specialized SQL servers
that provide advanced query language and query processing support for SQL queries
over star and snowflake schemas in a read-only environment.
“How are data actually stored in ROLAP and MOLAP architectures?” Let’s first look
at ROLAP. As its name implies, ROLAP uses relational tables to store data for online
analytical processing. Recall that the fact table associated with a base cuboid is referred
to as a base fact table. The base fact table stores data at the abstraction level indicated
by the join keys in the schema for the given data cube. Aggregated data can also be
stored in fact tables, referred to as summary fact tables. Some summary fact tables store
both base fact table data and aggregated data (see Example 3.10). Alternatively, separate
summary fact tables can be used for each abstraction level to store only aggregated data.
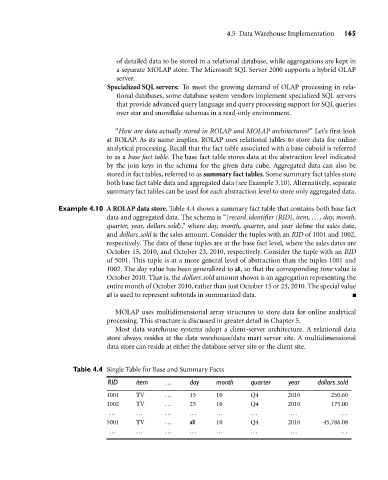
Example 4.10 A ROLAP data store. Table 4.4 shows a summary fact table that contains both base fact
data and aggregated data. The schema is “hrecord identifier (RID), item, ..., day, month,
quarter, year, dollars soldi,” where day, month, quarter, and year define the sales date,
and dollars sold is the sales amount. Consider the tuples with an RID of 1001 and 1002,
respectively. The data of these tuples are at the base fact level, where the sales dates are
October 15, 2010, and October 23, 2010, respectively. Consider the tuple with an RID
of 5001. This tuple is at a more general level of abstraction than the tuples 1001 and
1002. The day value has been generalized to all, so that the corresponding time value is
October 2010. That is, the dollars sold amount shown is an aggregation representing the
entire month of October 2010, rather than just October 15 or 23, 2010. The special value
all is used to represent subtotals in summarized data.
MOLAP uses multidimensional array structures to store data for online analytical
processing. This structure is discussed in greater detail in Chapter 5.
Most data warehouse systems adopt a client-server architecture. A relational data
store always resides at the data warehouse/data mart server site. A multidimensional
data store can reside at either the database server site or the client site.
Table 4.4 Single Table for Base and Summary Facts
RID item ... day month quarter year dollars sold
1001 TV ... 15 10 Q4 2010 250.60
1002 TV ... 23 10 Q4 2010 175.00
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
5001 TV ... all 10 Q4 2010 45,786.08
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...