Page 29 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 29
8 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
Start
Step 1
Structure the initial alternative/criteria decision matrix
Derive the normalized values to obtain the normalized matrix
Step 2: Obtain the weighted normalized decision matrix
Step 3: Obtaining the possible solutions as positive ideal and
negative ideal
Step 4: Determine the geometrical separation measures for the
alternatives to be ranked
Step 5: Find out the relative closeness to the ideal solution for
each alternative
Step 6: Determine the ranking of alternatives based on
preference order
NO Solution
obtained
YES
Stop
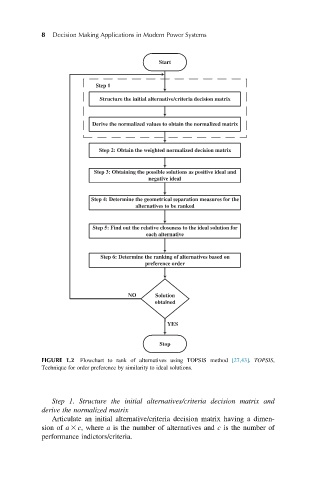
FIGURE 1.2 Flowchart to rank of alternatives using TOPSIS method [27,43]. TOPSIS,
Technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solutions.
Step 1. Structure the initial alternatives/criteria decision matrix and
derive the normalized matrix
Articulate an initial alternative/criteria decision matrix having a dimen-
sion of a 3 c, where a is the number of alternatives and c is the number of
performance indictors/criteria.