Page 174 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 174
Design for Six Sigma Project Algorithm 147
when the DFSS algorithm is employed. These reviews should not be
the only communication channel to the outside. Informal communi-
cation is found to be very beneficial to lessen the pressure of mile-
stone deadlines and other internal reviews.
■ Estimate workload associated with the DFSS algorithm activity.
Design workload is now estimated with reference to the planned
activities with the required timing.
■ Allocate resources for the various activities.
5.4 Understand Functional Requirements
Evolution (DFSS Algorithm Step 3)
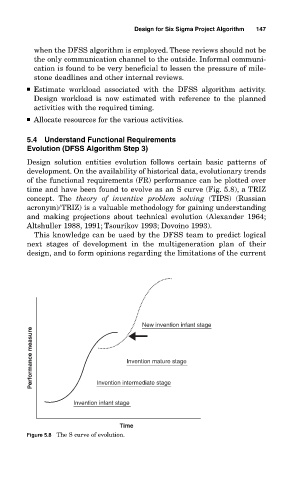
Design solution entities evolution follows certain basic patterns of
development. On the availability of historical data, evolutionary trends
of the functional requirements (FR) performance can be plotted over
time and have been found to evolve as an S curve (Fig. 5.8), a TRIZ
concept. The theory of inventive problem solving (TIPS) (Russian
acronym)/TRIZ) is a valuable methodology for gaining understanding
and making projections about technical evolution (Alexander 1964;
Altshuller 1988, 1991; Tsourikov 1993; Dovoino 1993).
This knowledge can be used by the DFSS team to predict logical
next stages of development in the multigeneration plan of their
design, and to form opinions regarding the limitations of the current
New invention infant stage
Performance measure Invention mature stage
Invention intermediate stage
Invention infant stage
Time
Figure 5.8 The S curve of evolution.