Page 325 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 325
8.3 Automation of Operation 311
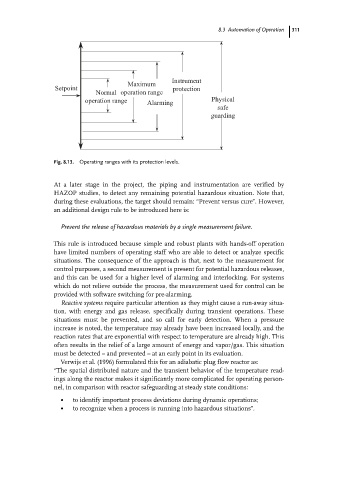
Instrument
Maximum
Setpoint protection
Normal operation range
operation range Alarming Physical
safe
guarding
Fig. 8.13. Operating ranges with its protection levels.
At a later stage in the project, the piping and instrumentation are verified by
HAZOP studies, to detect any remaining potential hazardous situation. Note that,
during these evaluations, the target should remain: ªPrevent versus cureº. However,
an additional design rule to be introduced here is:
Prevent the release of hazardous materials by a single measurement failure.
This rule is introduced because simple and robust plants with hands-off operation
have limited numbers of operating staff who are able to detect or analyze specific
situations. The consequence of the approach is that, next to the measurement for
control purposes, a second measurement is present for potential hazardous releases,
and this can be used for a higher level of alarming and interlocking. For systems
which do not relieve outside the process, the measurement used for control can be
provided with software switching for pre-alarming.
Reactive systems require particular attention as they might cause a run-away situa-
tion, with energy and gas release, specifically during transient operations. These
situations must be prevented, and so call for early detection. When a pressure
increase is noted, the temperature may already have been increased locally, and the
reaction rates that are exponential with respect to temperature are already high. This
often results in the relief of a large amount of energy and vapor/gas. This situation
must be detected ± and prevented ± at an early point in its evaluation.
Verwijs et al. (1996) formulated this for an adiabatic plug flow reactor as:
ªThe spatial distributed nature and the transient behavior of the temperature read-
ings along the reactor makes it significantly more complicated for operating person-
nel, in comparison with reactor safeguarding at steady state conditions:
. to identify important process deviations during dynamic operations;
. to recognize when a process is running into hazardous situationsº.