Page 102 - Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language
P. 102
Chapter 4 – PLANNING AND DRILLING A DEVELOPMENT WELL OFFSHORE 93
Drilling the Well
This example well will be drilled from a floating rig. A floating rig
moves with the tides, waves, and currents. Floating drilling requires
special equipment and techniques to deal with this movement.
Spudding the well and cementing the conductor
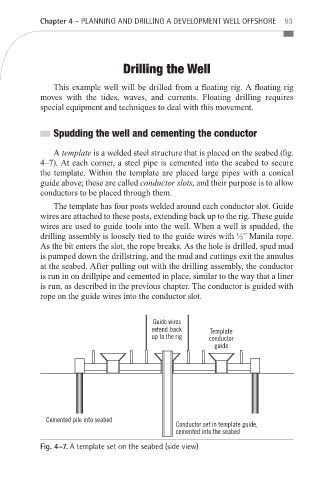
A template is a welded steel structure that is placed on the seabed (fig.
4–7). At each corner, a steel pipe is cemented into the seabed to secure
the template. Within the template are placed large pipes with a conical
guide above; these are called conductor slots, and their purpose is to allow
conductors to be placed through them.
The template has four posts welded around each conductor slot. Guide
wires are attached to these posts, extending back up to the rig. These guide
wires are used to guide tools into the well. When a well is spudded, the
drilling assembly is loosely tied to the guide wires with ½” Manila rope.
As the bit enters the slot, the rope breaks. As the hole is drilled, spud mud
is pumped down the drillstring, and the mud and cuttings exit the annulus
at the seabed. After pulling out with the drilling assembly, the conductor
is run in on drillpipe and cemented in place, similar to the way that a liner
is run, as described in the previous chapter. The conductor is guided with
rope on the guide wires into the conductor slot.
Fig. 4–7. A template set on the seabed (side view)
_Devereux_Book.indb 93 1/16/12 2:07 PM